Introduction: The Dawn of Smart Planting
Agriculture, the cornerstone of human civilization, is undergoing a profound transformation. We’re moving beyond traditional farming methods and embracing a new era of precision, efficiency, and sustainability. At the heart of this revolution lies smart planting technology, a convergence of cutting-edge innovations designed to optimize every stage of the planting process. This isn’t just about planting seeds; it’s about making informed decisions, minimizing waste, and maximizing yields in a way that respects our planet’s resources.
For generations, farmers have relied on intuition, experience, and often, guesswork. But in a world facing climate change, resource scarcity, and a growing population, we need a more intelligent approach. Smart planting offers that solution, providing farmers with the data, tools, and insights they need to thrive in a challenging environment. This comprehensive guide will delve into the depths of smart planting technology, exploring its benefits, components, implementation strategies, and future trends. Whether you’re a seasoned agricultural professional or simply curious about the future of food production, this is your roadmap to understanding and implementing smart planting.
Understanding Smart Planting Technology
Smart planting technology encompasses a wide range of tools and techniques that leverage data, automation, and connectivity to improve planting outcomes. It’s not a single, monolithic solution, but rather a collection of interconnected technologies that work together to optimize every aspect of the planting process. Let’s break down the key components:
1. Precision Seeding
Precision seeding is the foundation of smart planting. It involves using advanced equipment to place seeds at precise depths and spacing, ensuring optimal germination and growth. This is a far cry from traditional methods that often result in uneven plant populations and wasted seeds. Key technologies in precision seeding include:
- Variable Rate Seeding (VRS): VRS allows farmers to adjust seeding rates based on soil conditions, topography, and other factors. This ensures that each area of the field receives the optimal amount of seed, maximizing yield potential.
- GPS-Guided Planters: These planters use GPS technology to accurately place seeds, even in challenging terrain. They can also create detailed maps of planting locations, which can be used for future analysis and optimization.
- Single-Seed Placement: This technology ensures that each seed is placed individually, preventing overcrowding and competition for resources. It also reduces the need for thinning, saving time and labor.
2. Soil Monitoring and Analysis
Understanding soil conditions is crucial for successful planting. Smart planting technologies provide farmers with real-time data on soil moisture, nutrient levels, temperature, and other critical parameters. This information allows them to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and other inputs.
- Soil Sensors: These sensors can be buried in the ground or mounted on tractors to collect data on soil conditions. They transmit this data wirelessly to a central hub, where it can be analyzed and visualized.
- Remote Sensing: Satellites and drones can be used to capture images of fields, providing valuable information about soil health and plant growth. These images can be analyzed to identify areas of stress or nutrient deficiency.
- Soil Testing Laboratories: Traditional soil testing remains an important part of smart planting. However, advancements in laboratory technology have made it faster and easier to analyze soil samples and obtain detailed information about nutrient levels and other parameters.
3. Weather Monitoring and Forecasting
Weather plays a critical role in planting success. Smart planting technologies provide farmers with access to accurate weather forecasts, allowing them to plan planting operations around optimal conditions. This can help to minimize the risk of crop damage from frost, drought, or excessive rainfall.
- On-Site Weather Stations: These stations provide real-time data on temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed, and other weather parameters. They can be used to monitor local weather conditions and make informed decisions about planting and irrigation.
- Weather APIs: These APIs provide access to weather data from a variety of sources, including government agencies and private weather companies. Farmers can use this data to obtain accurate forecasts and plan their operations accordingly.
- Predictive Models: These models use historical weather data and other factors to predict future weather patterns. They can be used to assess the risk of extreme weather events and make informed decisions about crop management.
4. Data Analytics and Decision Support
The data collected by smart planting technologies is only valuable if it can be analyzed and used to make informed decisions. Data analytics and decision support tools help farmers to interpret this data and optimize their planting operations.
- Agricultural Software Platforms: These platforms integrate data from various sources, including soil sensors, weather stations, and planting equipment. They provide farmers with a centralized dashboard for monitoring crop health, managing inputs, and making informed decisions.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: These algorithms can be used to identify patterns in data and predict future outcomes. For example, they can be used to predict crop yields based on soil conditions, weather patterns, and planting practices.
- Decision Support Tools: These tools provide farmers with recommendations on how to optimize their planting operations based on data analysis. For example, they can recommend the optimal seeding rate for a particular field based on soil conditions and weather forecasts.
Benefits of Implementing Smart Planting Technology
The adoption of smart planting technology offers a multitude of advantages that extend beyond mere increased yields. It’s about creating a more sustainable, efficient, and resilient agricultural system. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
1. Increased Crop Yields
This is perhaps the most obvious benefit. By optimizing planting practices, farmers can ensure that each plant has the best possible chance of survival and growth. Precision seeding, coupled with soil monitoring and weather forecasting, creates the ideal environment for maximizing yields. Imagine reducing the guesswork and tailoring the planting process to the specific needs of each field. This targeted approach leads to healthier plants, reduced competition for resources, and ultimately, a more abundant harvest.
2. Reduced Input Costs
Smart planting helps farmers to use resources more efficiently. By precisely applying fertilizers, pesticides, and water only where and when they are needed, farmers can minimize waste and reduce their overall input costs. This not only saves money but also reduces the environmental impact of agriculture. Think of it as a surgical approach to resource management, eliminating the blanket applications that can be both costly and harmful.
3. Improved Resource Efficiency
Water scarcity is a growing concern around the world. Smart planting technologies can help farmers to use water more efficiently by monitoring soil moisture levels and irrigating only when necessary. This not only conserves water but also reduces the risk of over-watering, which can lead to root rot and other problems. Similarly, precise fertilizer application minimizes nutrient runoff, protecting waterways and reducing the need for costly remediation efforts.
4. Enhanced Soil Health
Sustainable agriculture depends on healthy soil. Smart planting technologies can help farmers to improve soil health by reducing tillage, promoting crop rotation, and applying organic amendments. Healthy soil is more resilient to drought, pests, and diseases, reducing the need for chemical inputs. It’s about nurturing the soil as a living ecosystem, creating a foundation for long-term productivity.
5. Reduced Environmental Impact
By reducing the use of fertilizers, pesticides, and water, smart planting can significantly reduce the environmental impact of agriculture. This is crucial for protecting our planet’s resources and ensuring a sustainable food supply for future generations. It’s about moving towards a more responsible and environmentally conscious approach to farming.
6. Better Decision-Making
Smart planting provides farmers with access to a wealth of data that can be used to make informed decisions about crop management. This data can help farmers to identify problems early on and take corrective action before they escalate. It’s about empowering farmers with the knowledge they need to succeed in a challenging environment. Imagine having a real-time view of your crops’ health and being able to respond proactively to any issues that arise.
7. Increased Profitability
Ultimately, the goal of any business is to make a profit. Smart planting can help farmers to increase their profitability by increasing yields, reducing input costs, and improving resource efficiency. This makes agriculture a more sustainable and attractive career path for young people. It’s about ensuring the long-term viability of farming as a profession.
Implementing Smart Planting Technology: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing smart planting technology is not a one-size-fits-all process. It requires careful planning, assessment, and a tailored approach based on your specific needs and resources. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Assess Your Needs and Goals
Before investing in any smart planting technology, it’s important to assess your current farming practices and identify areas where you can improve. What are your biggest challenges? Are you struggling with low yields, high input costs, or environmental concerns? What are your goals for implementing smart planting technology? Do you want to increase yields, reduce costs, or improve sustainability? Answering these questions will help you to prioritize your investments and choose the technologies that are most relevant to your needs.
2. Conduct a Soil Analysis
Understanding your soil is crucial for successful planting. Conduct a thorough soil analysis to determine the nutrient levels, pH, and other important parameters. This will help you to choose the right fertilizers and other inputs, as well as to optimize your planting practices. Consider both traditional laboratory testing and the use of soil sensors for real-time monitoring.
3. Choose the Right Technology
There are many different smart planting technologies available on the market, so it’s important to choose the ones that are right for your farm. Consider your budget, your technical expertise, and your specific needs. Start with the basics, such as precision seeding and soil monitoring, and then gradually add more advanced technologies as you become more comfortable. Don’t feel pressured to adopt every technology at once. A phased approach is often the most effective.
4. Integrate Your Data
The key to successful smart planting is integrating data from various sources, including soil sensors, weather stations, and planting equipment. This will give you a comprehensive view of your farming operations and allow you to make informed decisions. Choose an agricultural software platform that can integrate data from multiple sources and provide you with a user-friendly interface.
5. Train Your Staff
Smart planting technology is only as good as the people who use it. Make sure that your staff is properly trained on how to use the new technologies and interpret the data they provide. Provide ongoing training and support to ensure that your staff is comfortable and confident using the technology. Consider partnering with local agricultural extension offices or technology providers for training resources.
6. Start Small and Scale Up
Don’t try to implement smart planting technology across your entire farm at once. Start with a small pilot project and gradually scale up as you gain experience and confidence. This will allow you to learn from your mistakes and refine your approach before making a large investment. Choose a representative field for your pilot project and carefully monitor the results.
7. Monitor and Evaluate Your Results
It’s important to monitor and evaluate your results to determine whether smart planting technology is actually improving your farming operations. Track your yields, input costs, and environmental impact. Use this data to refine your practices and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review your data and compare it to previous years to assess the impact of the new technologies.
8. Seek Expert Advice
Implementing smart planting technology can be complex, so don’t be afraid to seek expert advice. Consult with agricultural consultants, technology providers, and other farmers who have experience with smart planting. Attend workshops and conferences to learn about the latest trends and best practices. Building a network of knowledgeable advisors can be invaluable.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of smart planting are undeniable, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
1. Initial Investment Costs
The initial investment in smart planting technology can be significant. Sensors, software, and precision equipment can be expensive, making it difficult for smallholder farmers to adopt these technologies. However, government subsidies, grants, and financing options can help to offset these costs. Consider the long-term return on investment when evaluating the cost of smart planting technology.
2. Technical Expertise
Operating and maintaining smart planting technology requires a certain level of technical expertise. Farmers may need to invest in training or hire specialized staff to manage the technology. However, many technology providers offer training and support services to help farmers get started. Look for user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive support documentation.
3. Data Privacy and Security
Smart planting technology generates a lot of data, which raises concerns about data privacy and security. Farmers need to be aware of how their data is being used and protected. Choose technology providers that have strong data privacy policies and security measures in place. Consider encrypting your data and limiting access to authorized personnel.
4. Connectivity Issues
Many smart planting technologies rely on internet connectivity, which can be a challenge in rural areas. Farmers may need to invest in improved internet infrastructure to ensure reliable connectivity. Consider using satellite-based internet or other alternative solutions. Look for technologies that can operate offline or with limited connectivity.
5. Interoperability
Different smart planting technologies may not be compatible with each other, making it difficult to integrate data from various sources. Choose technologies that are based on open standards and can be easily integrated with other systems. Look for platforms that support APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for seamless data exchange.
The Future of Smart Planting Technology
Smart planting technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations emerging all the time. Here are some of the key trends to watch:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are being used to develop more sophisticated decision support tools that can help farmers to optimize their planting practices. These tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict future outcomes, allowing farmers to make more informed decisions.
2. Robotics and Automation
Robots are being used to automate various planting tasks, such as seeding, weeding, and harvesting. This can help to reduce labor costs and improve efficiency. Autonomous tractors and drones are also becoming increasingly common.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT is connecting various agricultural devices and sensors, creating a vast network of data that can be used to optimize planting practices. This includes sensors that monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and plant health.
4. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is being used to improve the traceability and transparency of the food supply chain. This can help to build trust between farmers and consumers and ensure that food is produced sustainably.
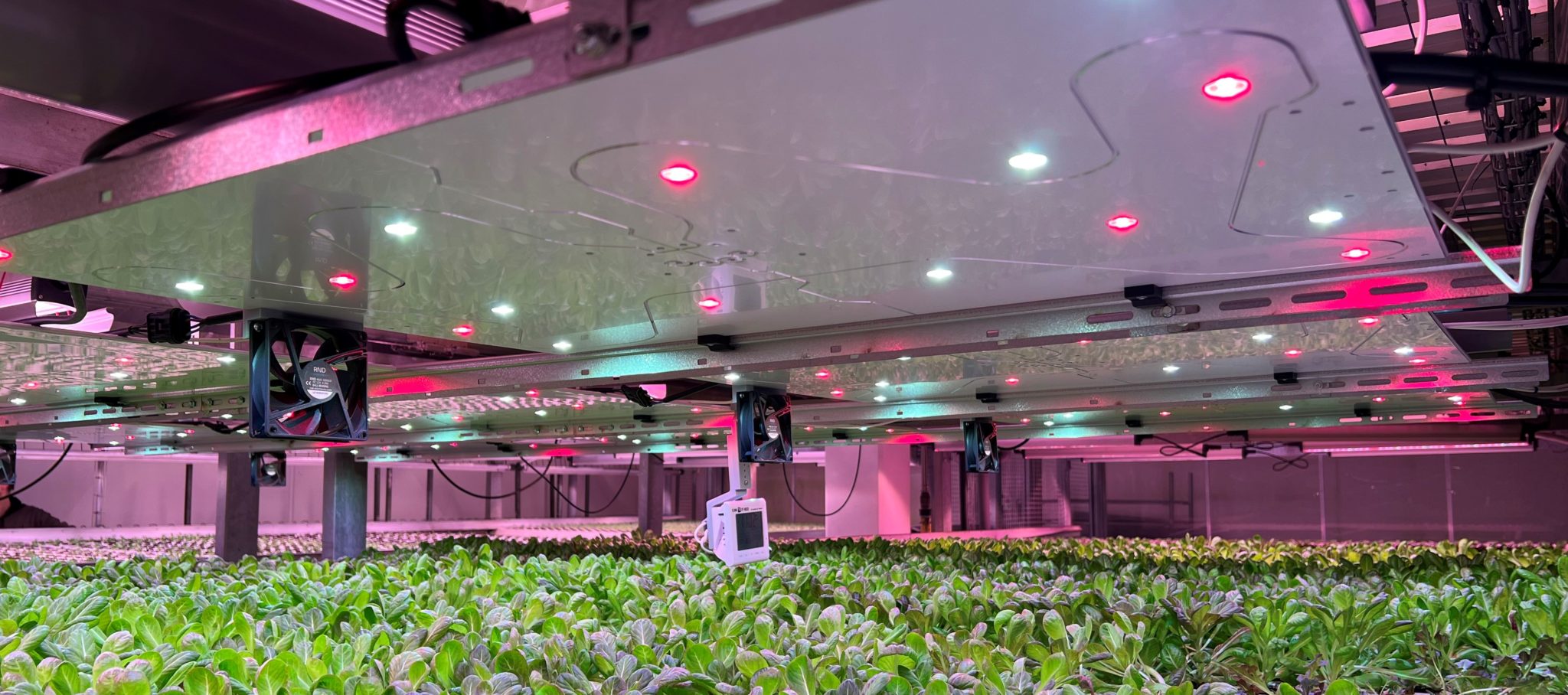
5. Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is a new approach to agriculture that involves growing crops in stacked layers, often indoors. This can help to increase yields and reduce the environmental impact of agriculture. Smart planting technologies are being used to optimize the growing conditions in vertical farms.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Agriculture
Smart planting technology is revolutionizing agriculture, offering farmers the opportunity to increase yields, reduce costs, and improve sustainability. By embracing these technologies, we can create a more resilient and efficient food system that can meet the challenges of the 21st century. While there are challenges to overcome, the benefits of smart planting are undeniable. By carefully planning, implementing, and evaluating our approach, we can unlock the full potential of these technologies and create a brighter future for agriculture.
The journey towards smart planting is a continuous process of learning, adaptation, and innovation. As technology evolves and our understanding of agricultural systems deepens, we can expect even more transformative solutions to emerge. By staying informed, embracing new ideas, and collaborating with experts, we can ensure that agriculture remains a vital and sustainable industry for generations to come. Let’s embrace the future of agriculture and work together to create a world where everyone has access to safe, nutritious, and sustainably produced food.