The Urgent Need for Native Plant Restoration
Our planet is facing an unprecedented crisis. From climate change to habitat loss, the challenges are immense. But amidst these daunting issues, there’s a beacon of hope: native plant restoration. It’s a powerful tool, a critical component of a larger strategy to heal our ecosystems and secure a healthier future for all living things. But what exactly does this entail? And why is it so incredibly vital right now?
Native plant restoration is, at its core, the practice of re-establishing plant communities that have been degraded, damaged, or destroyed. This could be due to a variety of factors, from invasive species outcompeting the local flora to the impact of human development and agriculture. The goal is simple: to bring back the plants that naturally belong in a specific area, the ones that have evolved over millennia to thrive in that particular environment. This goes beyond just planting some flowers; it’s a holistic approach that considers the entire ecosystem, from the soil and the insects to the birds and the mammals.
The importance of native plant restoration cannot be overstated. These plants are the foundation of a healthy ecosystem. They provide food and shelter for a vast array of wildlife, from tiny pollinators to large mammals. They help to purify the air and water, prevent soil erosion, and even regulate the climate. When native plants disappear, the entire ecosystem suffers, leading to a cascade of negative consequences. It’s like pulling out a key piece of a complex puzzle – the whole picture becomes distorted and incomplete.
Understanding the Benefits: Why Native Plants Matter
The benefits of native plant restoration are far-reaching and touch upon nearly every aspect of our lives. Let’s delve into some of the most significant advantages:
Biodiversity Boost
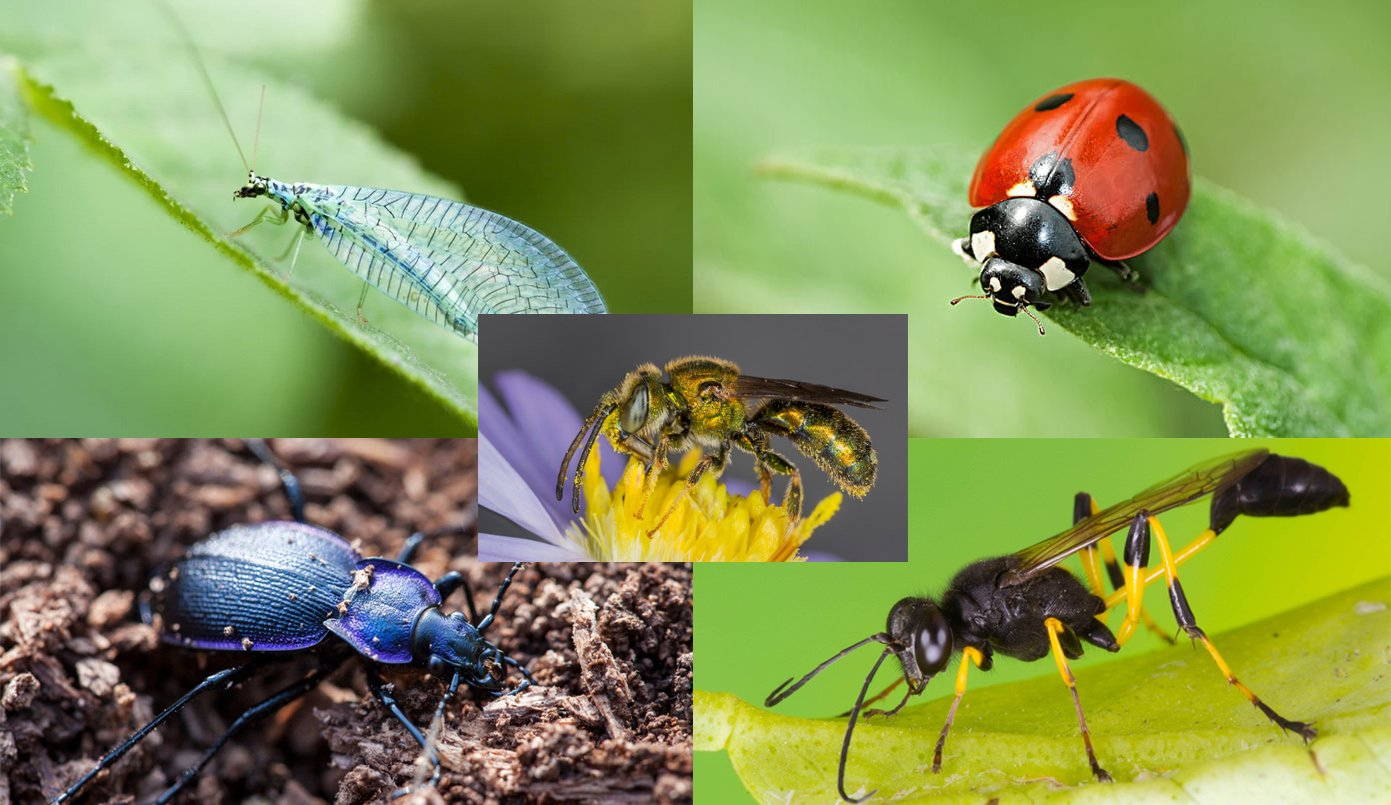
One of the most immediate and obvious benefits is the increase in biodiversity. Native plants support a wider range of wildlife than non-native species. They have co-evolved with local insects, birds, and other animals, providing the specific food sources and habitats these creatures need to survive. When native plants are restored, the animals that depend on them flourish as well. This creates a more resilient and diverse ecosystem, better equipped to withstand environmental stressors.
Ecosystem Services Enhancement
Ecosystem services are the essential benefits that ecosystems provide to humans, such as clean air and water, pollination, and climate regulation. Native plants are crucial for maintaining and enhancing these services. They help to filter pollutants from the air and water, prevent soil erosion, and sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. By restoring native plant communities, we are essentially investing in a healthier environment for ourselves and future generations.
Wildlife Habitat Creation and Improvement
Native plants provide superior habitat for native wildlife. They offer food, shelter, and nesting sites that non-native plants often lack. For example, many native insects rely on specific native plants for their survival. When these plants are present, the insects thrive, and in turn, provide food for birds, amphibians, and other animals. Restoring native plants can help to reverse the decline of many wildlife populations, including endangered and threatened species.
Reduced Need for Pesticides and Fertilizers
Native plants are adapted to the local environment and are often more resistant to pests and diseases than non-native plants. This means that they require less maintenance and fewer interventions, such as pesticides and fertilizers. By using native plants, we can reduce our reliance on these harmful chemicals, which can pollute our water, harm wildlife, and pose risks to human health.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
Native plants play a vital role in mitigating climate change. They absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their roots, stems, and leaves. They also help to regulate the local climate by providing shade and reducing the urban heat island effect. Restoring native plant communities can help to reduce the impacts of climate change and make our communities more resilient to its effects.
Aesthetics and Community Engagement
Native plants can be incredibly beautiful, adding color, texture, and interest to our landscapes. They can also provide a sense of place and connect us to the natural world. Native plant restoration projects often involve community engagement, such as volunteer planting events and educational workshops. This can foster a sense of stewardship and encourage people to take action to protect their local environment.
The Challenges in Native Plant Restoration
While the benefits of native plant restoration are clear, it’s not always an easy undertaking. There are several challenges that restoration efforts often face:
Invasive Species Control
One of the biggest hurdles is the control of invasive species. These non-native plants can outcompete native plants for resources, such as sunlight, water, and nutrients. They can also alter the soil chemistry and disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem. Effective invasive species control is essential for successful native plant restoration. This may involve manual removal, herbicide application, or biological control methods, depending on the specific species and the scale of the project.
Seed and Plant Sourcing
Finding the right seeds and plants can also be a challenge. It’s important to source seeds and plants that are genetically appropriate for the local area. This means that they should be from the same ecoregion and have adapted to the specific environmental conditions. Sourcing can be difficult, as some native plant species may be rare or unavailable in the quantities needed for restoration projects. This often requires working with specialized nurseries or seed banks.
Site Preparation and Maintenance
Preparing the site for planting can be a significant undertaking. This may involve removing existing vegetation, amending the soil, and creating favorable growing conditions. Once the plants are in the ground, ongoing maintenance is essential. This includes watering, weeding, and protecting the plants from pests and diseases. The level of maintenance required will depend on the specific site conditions and the species being planted.
Funding and Resources
Native plant restoration projects often require funding and resources. This can include money for seeds, plants, tools, and labor. Securing funding can be competitive, and projects may need to rely on grants, donations, or volunteer support. Access to expertise and technical assistance can also be a challenge, especially for smaller organizations or community groups.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about the importance of native plant restoration is crucial for building support and encouraging participation. This involves educating people about the benefits of native plants, the threats to ecosystems, and the actions that can be taken to make a difference. Public education can help to generate enthusiasm for restoration projects and encourage people to get involved.
Strategies for Successful Native Plant Restoration
Despite the challenges, many successful native plant restoration projects are underway around the world. Here are some key strategies that contribute to their success:
Thorough Planning and Assessment
Before starting any restoration project, it’s essential to conduct a thorough assessment of the site and the surrounding ecosystem. This should include identifying the native plant species that were historically present, assessing the current conditions, and determining the goals of the restoration project. This information will inform the selection of appropriate plants, the site preparation methods, and the ongoing management strategies.
Invasive Species Management
Controlling invasive species is often the first and most critical step in native plant restoration. This may involve a combination of methods, such as manual removal, herbicide application, and biological control. The specific approach will depend on the species being targeted and the scale of the project. It’s important to develop a comprehensive management plan and implement it consistently over time.
Seed Collection and Propagation
Collecting seeds from local native plant populations and propagating them in nurseries is an important way to ensure that the restoration project has access to the right plants. This approach helps to preserve the genetic diversity of the native plant species and ensures that the plants are adapted to the local environment. Seed collection and propagation can be a time-consuming process, but it’s often necessary to obtain the quantities of plants needed for large-scale restoration projects.
Site Preparation and Planting Techniques
Proper site preparation is essential for creating favorable growing conditions for native plants. This may involve removing existing vegetation, amending the soil, and creating drainage systems. The planting techniques will vary depending on the species being planted and the site conditions. It’s important to follow best practices for planting, such as proper spacing, watering, and mulching.
Monitoring and Adaptive Management
Monitoring the progress of the restoration project is crucial for evaluating its success and making adjustments as needed. This may involve tracking the survival and growth of the planted species, monitoring the presence of invasive species, and assessing the overall health of the ecosystem. Based on the monitoring results, the management plan can be adapted to address any challenges or take advantage of new opportunities.
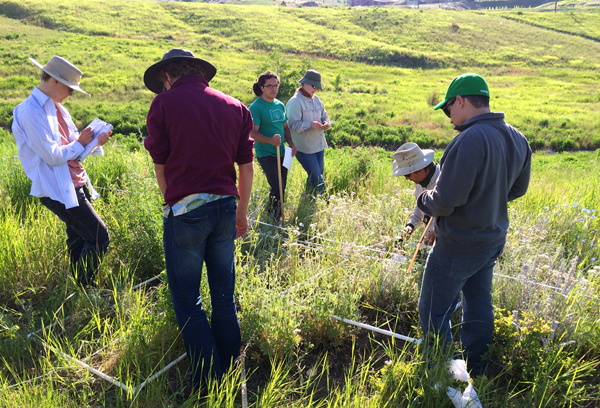
Community Engagement and Education
Involving the community in the restoration project is essential for building support and ensuring its long-term success. This may involve volunteer planting events, educational workshops, and public outreach campaigns. Engaging the community can help to raise awareness about the importance of native plant restoration and encourage people to take action to protect their local environment.
Case Studies: Inspiring Examples of Native Plant Restoration
To truly grasp the impact of native plant restoration, let’s examine some inspiring examples from around the globe:
The Tallgrass Prairie Restoration, USA
The tallgrass prairie, once a vast ecosystem stretching across the American Midwest, has been dramatically reduced by agriculture and development. Dedicated efforts are underway to restore fragments of this iconic landscape. These projects involve planting native grasses and wildflowers, controlling invasive species, and reintroducing fire, a natural process that helps to maintain the prairie ecosystem. The results have been remarkable, with increased biodiversity, improved soil health, and the return of iconic prairie wildlife.
The Coastal Dune Restoration, Australia
Coastal dunes are essential for protecting coastlines from erosion and providing habitat for a wide range of plants and animals. In Australia, many coastal dunes have been degraded by human activities, such as development and recreational use. Restoration projects involve planting native dune vegetation, such as spinifex grass and coastal wattle, to stabilize the dunes and prevent erosion. These projects have not only protected the coastlines but have also created valuable habitat for native wildlife.
The Rainforest Restoration, Costa Rica
Costa Rica is renowned for its biodiversity, but deforestation has threatened its rainforests. Restoration efforts are underway to reforest degraded areas and connect fragmented forest patches. These projects involve planting native tree species, controlling invasive plants, and promoting natural regeneration. The results have been transformative, with increased forest cover, improved water quality, and the return of iconic rainforest species, such as monkeys and jaguars.
How You Can Get Involved in Native Plant Restoration
Native plant restoration is not just the domain of scientists and conservationists; it’s a cause that anyone can contribute to. Here’s how you can make a difference:
Volunteer at a Local Restoration Project
Many organizations and community groups organize native plant restoration projects. Volunteering is a great way to get hands-on experience, learn about native plants, and contribute to a worthy cause. Tasks may include planting, weeding, seed collection, and monitoring.
Plant Native Plants in Your Yard
One of the simplest and most effective ways to support native plant restoration is to plant native plants in your own yard. This provides habitat for wildlife, reduces the need for pesticides and fertilizers, and enhances the beauty of your landscape. Research the native plants that are suitable for your local area and choose plants that are appropriate for the site conditions.
Support Native Plant Nurseries and Organizations
Support local nurseries and organizations that specialize in native plants. This helps to ensure that the plants are sourced responsibly and that the restoration efforts are supported. Consider donating to organizations that are working to protect and restore native ecosystems.
Educate Yourself and Others
Learn about the importance of native plant restoration and share your knowledge with others. Talk to your friends, family, and neighbors about the benefits of native plants and the threats to ecosystems. Encourage them to take action to protect their local environment.
Advocate for Native Plant Restoration
Contact your elected officials and advocate for policies that support native plant restoration. This may include funding for restoration projects, regulations to protect native habitats, and incentives for planting native plants. Your voice can make a difference.
The Future of Native Plant Restoration
The future of native plant restoration is bright. As awareness of the importance of healthy ecosystems grows, so does the commitment to restoring them. Technological advancements, such as remote sensing and genetic analysis, are providing new tools for understanding and managing ecosystems. Collaboration between scientists, conservationists, and community members is becoming increasingly common, leading to more effective and sustainable restoration efforts.
The fight to restore native plants is a fight for the future of our planet. It’s a fight for biodiversity, for clean air and water, and for a healthy and resilient environment. It’s a fight that requires the dedication and collaboration of people from all walks of life. By embracing native plant restoration, we can build a brighter and more sustainable future for ourselves and for generations to come.
Native plant restoration is more than just a trend; it’s a necessity. It’s about recognizing the intrinsic value of our natural world and taking action to protect and restore it. By understanding the benefits, addressing the challenges, and implementing effective strategies, we can make a significant difference in the health of our planet. Let’s join forces, plant the seeds of change, and watch our ecosystems flourish once again.