Unlock the Secrets of Composting: A Guide to Transforming Garden Waste into Black Gold
Ah, the garden. A place of tranquility, vibrant life, and, let’s be honest, a constant stream of… well, waste. From fallen leaves and spent blooms to unruly weeds and leftover vegetable scraps, our gardens generously provide a wealth of organic material. But what if I told you that this ‘waste’ isn’t actually waste at all? What if I told you it’s a treasure trove, a source of incredible potential, and the key to unlocking the healthiest, most vibrant garden you’ve ever imagined?
That’s where composting comes in. Composting is more than just a trendy gardening practice; it’s a fundamental process, a natural cycle of decomposition that transforms organic matter into a rich, dark, crumbly substance often called ‘black gold.’ This isn’t just any soil amendment; it’s packed with nutrients, improves soil structure, and supports a thriving ecosystem in your garden. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of composting, exploring various methods, techniques, and tips to help you transform your garden waste into a valuable resource. Prepare to revolutionize your gardening journey!
Why Compost? The Benefits Beyond the Bin
Before we dive into the ‘how,’ let’s talk about the ‘why.’ Why should you bother with composting? What are the tangible benefits that make it worth the effort? The answer, my friend, is multifaceted. Composting offers a wealth of advantages for your garden, the environment, and even your wallet. Let’s break it down:
- Enhances Soil Health: This is perhaps the most significant benefit. Compost acts as a superfood for your soil, improving its structure, aeration, and water retention. It helps break up heavy clay soils, making them easier to work with, and improves the drainage of sandy soils.
- Nutrient-Rich: Compost is teeming with essential nutrients that plants need to thrive. It slowly releases these nutrients, providing a steady supply of nourishment over time. This reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, which can be harmful to the environment.
- Reduces the Need for Chemical Fertilizers: Compost provides a natural and sustainable alternative to synthetic fertilizers. By using compost, you can reduce your reliance on these potentially harmful chemicals, minimizing their impact on the environment and the health of your garden.
- Improves Water Retention: Compost acts like a sponge, holding onto water and slowly releasing it to plant roots. This is especially beneficial in dry climates, as it reduces the need for frequent watering and helps conserve water resources.
- Suppresses Plant Diseases and Pests: Healthy soil is the foundation of healthy plants. Compost strengthens plants’ natural defenses, making them more resistant to diseases and pests.
- Reduces Waste: Composting is a fantastic way to reduce the amount of waste you send to landfills. By diverting your garden waste, you’re contributing to a more sustainable lifestyle and reducing your environmental footprint.
- Saves Money: While there may be some initial costs associated with setting up a composting system, the long-term benefits are undeniable. You’ll save money on fertilizers, soil amendments, and potentially even water bills.
- Environmentally Friendly: Composting is a sustainable practice that benefits the environment in numerous ways. It reduces greenhouse gas emissions from landfills, conserves water, and promotes healthy soil ecosystems.
As you can see, the benefits of composting are far-reaching. It’s a win-win situation for your garden and the planet. Now, let’s get down to the nitty-gritty of how to make this magic happen.
Composting Methods: Choosing the Right Approach for Your Garden
The beauty of composting is that there’s a method for everyone, regardless of your space, time commitment, or level of gardening experience. Here are some of the most popular and effective composting methods:
1. The Traditional Compost Pile
This is the classic method, often visualized as a large, open pile of organic matter. It’s a simple and effective approach, especially suitable for larger gardens with ample space. Here’s how it works:
- Location: Choose a level, well-drained area in your garden. It’s best to locate the pile in a partially shaded area to prevent it from drying out too quickly.
- Materials: You’ll need a mix of ‘greens’ (nitrogen-rich materials) and ‘browns’ (carbon-rich materials). Greens include grass clippings, vegetable scraps, and coffee grounds. Browns include dried leaves, straw, and shredded paper.
- Layering: Start with a layer of browns at the bottom, followed by a layer of greens. Alternate layers, aiming for a ratio of roughly 2:1 or 3:1 browns to greens.
- Moisture: Keep the pile moist, like a wrung-out sponge. Add water as needed, especially during dry periods.
- Turning: Turn the pile regularly, ideally every week or two. This aerates the compost, providing oxygen to the microorganisms that break down the organic matter.
- Time: With regular turning and proper moisture, your compost should be ready in 6-12 months.
Pros: Simple, inexpensive, and suitable for large volumes of waste.
Cons: Can be unsightly, requires regular turning, and may attract pests if not managed properly.
2. The Compost Bin
Compost bins come in various shapes and sizes, from simple wire mesh enclosures to more sophisticated plastic or wooden bins. They offer a more contained and organized approach to composting.
- Types: Choose a bin that suits your needs and budget. Consider factors like size, ease of access, and pest resistance.
- Materials: Similar to the traditional pile, you’ll need a mix of greens and browns.
- Layering and Maintenance: Layer your materials and maintain moisture levels as you would with a traditional pile. Turning the compost is still important, but some bins are designed to make this easier.
- Time: Compost in a bin typically takes 6-12 months to mature.
Pros: More organized, tidier appearance, and better pest control.
Cons: Can be more expensive than a traditional pile, may require more effort to turn the compost.
3. The Tumbler
Compost tumblers are enclosed containers that are designed to be rotated, making turning the compost effortless. They’re a great option for those who want a quick and easy composting process.
- Design: Tumblers come in various sizes and designs, but they all feature a rotating drum.
- Materials: Use a mix of greens and browns, just like with other methods.
- Turning: Simply crank the tumbler a few times every few days to aerate the compost.
- Time: Tumblers can produce compost in as little as 4-8 weeks due to the increased aeration and heat.
Pros: Fast composting process, easy to turn, and less labor-intensive.
Cons: Can be more expensive than other methods, and may have a smaller capacity.
4. Vermicomposting (Worm Composting)
This fascinating method utilizes red wiggler worms to break down organic matter. It’s ideal for small spaces, such as apartments or balconies, and produces a nutrient-rich compost known as ‘worm castings.’
- Setup: You’ll need a worm bin, which can be purchased or built yourself.
- Worms: Red wiggler worms are the stars of the show. They’re voracious eaters and excellent composters.
- Food: Feed the worms a diet of food scraps, such as vegetable and fruit peelings, coffee grounds, and tea bags. Avoid meat, dairy, and oily foods.
- Maintenance: Keep the bin moist and ensure the worms have a comfortable environment.
- Harvesting: After a few months, you can harvest the worm castings, which are an excellent soil amendment.
Pros: Produces high-quality compost, ideal for small spaces, and relatively odor-free.
Cons: Requires more initial setup and ongoing maintenance, and requires a bit of learning curve.
5. Bokashi Composting
Bokashi composting is a unique method that uses a special bran inoculated with beneficial microorganisms to ferment food waste. It’s particularly effective for handling all types of food waste, including meat, dairy, and cooked foods.
- Process: Food waste is layered with bokashi bran in an airtight container.
- Fermentation: The bran encourages fermentation, which breaks down the food waste.
- End Product: The fermented food waste can be buried in the garden or added to a compost pile.
- Benefits: Bokashi composting reduces odors, prevents pest problems, and can handle a wider variety of food waste.
Pros: Handles all food waste, reduces odors, and produces a nutrient-rich soil amendment.
Cons: Requires bokashi bran, and the fermented waste needs to be buried or added to a compost pile.
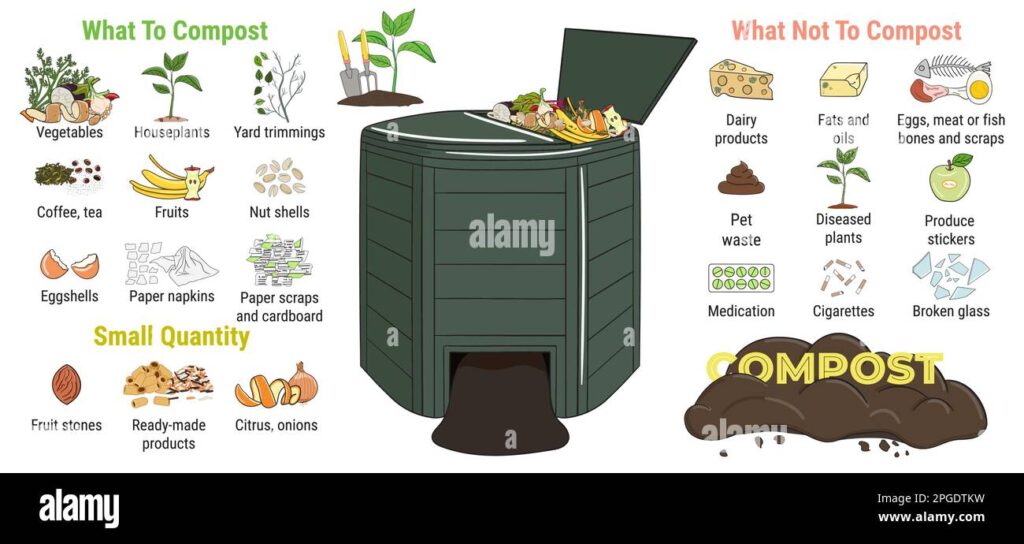
What to Compost: The Green and Brown Essentials
Now that you’re familiar with the different composting methods, let’s talk about the materials you can use. The key is to understand the difference between ‘greens’ and ‘browns’ and to maintain a balanced ratio. Here’s a breakdown:
Greens (Nitrogen-Rich Materials)
- Grass Clippings: Freshly cut grass is an excellent source of nitrogen.
- Vegetable Scraps: Peelings, cores, and trimmings from your fruits and vegetables.
- Fruit Waste: Overripe fruit, fruit peels, and cores.
- Coffee Grounds and Tea Bags: These are rich in nitrogen and nutrients.
- Manure: Animal manure (from herbivores only) can be a valuable source of nutrients. Be sure to age the manure properly before adding it to your compost.
- Weeds: Pull weeds before they go to seed and add them to the compost pile.
- Plant Trimmings: Prunings from your plants, flowers, and shrubs.
Browns (Carbon-Rich Materials)
- Dried Leaves: Fallen leaves are a classic ‘brown’ material.
- Straw and Hay: These provide excellent aeration and carbon.
- Shredded Paper and Cardboard: Shredded paper and cardboard add bulk and carbon to the mix.
- Wood Chips and Sawdust: These are slow to decompose but add valuable carbon.
- Twigs and Small Branches: Chop them into smaller pieces to speed up decomposition.
Important Note: Avoid composting meat, dairy products, oily foods, diseased plants, and pet waste in a traditional compost pile, as these can attract pests and create unpleasant odors. With Bokashi composting, this is less of a concern.
Composting Tips and Troubleshooting: Your Path to Black Gold
Composting is a relatively straightforward process, but there are a few tips and troubleshooting techniques that can help you achieve optimal results:
- Chop it Up: Smaller pieces decompose faster. Chop or shred larger materials like leaves, branches, and cardboard.
- Maintain the Right Ratio: Aim for a balance of browns and greens, typically around a 2:1 or 3:1 ratio of browns to greens.
- Keep it Moist: Your compost pile should be moist, like a wrung-out sponge. Add water as needed, especially during dry periods.
- Turn Regularly: Turning the pile aerates the compost, providing oxygen to the microorganisms and speeding up the decomposition process.
- Monitor the Temperature: The temperature of your compost pile is an indicator of its activity. A healthy pile will heat up as the microorganisms break down the organic matter.
- Avoid Overcrowding: Don’t overload your compost pile with too much material at once. Add materials gradually, allowing the microorganisms to break them down.
- Troubleshooting Common Problems:
- Smelly Compost: This usually indicates a lack of oxygen. Turn the pile more frequently and add more browns.
- Slow Decomposition: This could be due to a lack of moisture, a poor balance of greens and browns, or a lack of oxygen. Adjust your methods accordingly.
- Pests: If pests are a problem, ensure you are not composting meat, dairy, or oily foods. Bury food scraps in the center of the pile.
Using Your Compost: Harvesting the Rewards
Once your compost has matured, it’s time to harvest the rewards of your labor! Here’s how to tell when your compost is ready and how to use it:
- Signs of Readiness: Mature compost should be dark, crumbly, and smell earthy. You should no longer be able to identify the original materials.
- Harvesting: If you’re using a traditional pile, you can harvest the finished compost from the bottom of the pile, where the decomposition process is most advanced. For bins and tumblers, the process is usually more straightforward.
- Using Compost in Your Garden:
- Soil Amendment: Mix compost into your garden soil to improve its structure, aeration, and nutrient content.
- Mulch: Use compost as a mulch around plants to suppress weeds, retain moisture, and provide nutrients.
- Potting Mix: Mix compost with other ingredients, such as peat moss or perlite, to create a nutrient-rich potting mix.
Application Rates: The amount of compost you use will depend on your soil type and the needs of your plants. A general guideline is to apply a 1-2 inch layer of compost to your garden beds each year. You can also use compost in your containers, but make sure it’s well-aged before using it.
Composting Beyond the Basics: Expanding Your Knowledge
Once you’ve mastered the basics of composting, you can explore more advanced techniques and ideas:
- Hot Composting: This method involves maintaining a high temperature in your compost pile to speed up the decomposition process.
- Compost Tea: Brew compost tea by steeping compost in water. This creates a nutrient-rich liquid that can be used as a foliar spray or soil drench.
- Composting with Different Materials: Experiment with composting different materials, such as wool scraps, coffee chaff, and seaweed.
- Building a Composting System: Design and build your own composting system to fit your specific needs and space constraints.
Conclusion: Embrace the Cycle of Nature
Composting is more than just a gardening chore; it’s a way to connect with nature, reduce waste, and create a healthier, more sustainable garden. By understanding the principles of composting and choosing the right method for your needs, you can transform your garden waste into a valuable resource and unlock the secrets of ‘black gold.’ So, get out there, start composting, and watch your garden flourish!
Happy composting!


