Green Roof Planting Specifications: A Comprehensive Guide to Thriving Rooftop Ecosystems
Embarking on a green roof project is an exciting endeavor, a blend of environmental responsibility and architectural innovation. But before you can bask in the beauty of your rooftop garden, a thorough understanding of green roof planting specifications is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into every aspect, from initial planning to long-term maintenance, ensuring your green roof flourishes and provides the myriad benefits it promises. We’ll explore the intricacies of plant selection, substrate composition, drainage systems, and much more. Let’s dive in and unlock the secrets to a successful green roof!
Understanding the Fundamentals of Green Roofs
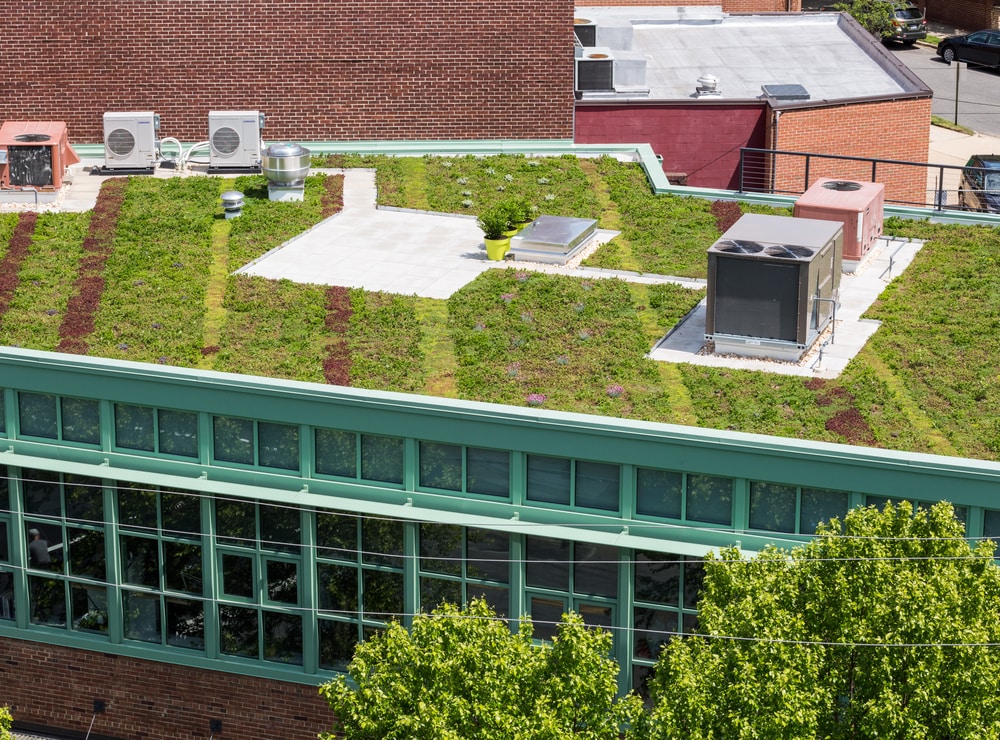
A green roof, also known as a vegetated roof, is essentially a layer of vegetation installed on top of a building’s roof. It’s more than just a pretty aesthetic; it’s a sophisticated ecosystem designed to work in harmony with the environment. Green roofs offer a multitude of advantages, making them increasingly popular in both residential and commercial settings. These benefits include:
- Improved Insulation: Green roofs act as a natural insulator, reducing heating and cooling costs.
- Stormwater Management: They absorb rainwater, reducing runoff and the strain on drainage systems.
- Enhanced Air Quality: Plants filter pollutants, improving the air quality in urban environments.
- Habitat Creation: Green roofs provide valuable habitats for birds, insects, and other wildlife.
- Extended Roof Lifespan: The vegetation protects the underlying roofing membrane from UV radiation and extreme temperatures, extending its lifespan.
- Aesthetic Appeal: They transform ordinary rooftops into beautiful, green spaces.
Before you start planting, it’s essential to understand the different types of green roofs. The two primary categories are:
- Extensive Green Roofs: These are typically lightweight, low-maintenance systems designed for minimal intervention. They usually feature drought-tolerant plants like sedums and require less frequent irrigation.
- Intensive Green Roofs: These are more complex systems that can support a wider variety of plants, including shrubs, trees, and even small gardens. They require more intensive maintenance, including regular watering, fertilization, and pruning.
Planning and Design: Laying the Groundwork for Success
Careful planning is the cornerstone of a successful green roof project. This stage involves assessing the roof’s structural capacity, selecting appropriate plants, and designing the drainage and irrigation systems. Here’s a breakdown of the key considerations:
Structural Assessment
The first and foremost step is to assess the structural integrity of your roof. A structural engineer must evaluate the roof’s load-bearing capacity to ensure it can support the added weight of the green roof system, including the substrate, plants, and any accumulated rainwater. This assessment is critical; overloading the roof can lead to serious structural damage.
Plant Selection: Choosing the Right Green Roof Vegetation
Choosing the right plants is pivotal to the long-term success and beauty of your green roof. The selection process should consider several factors:
- Climate: Select plants that are well-suited to your local climate conditions, including temperature, rainfall, and sunlight exposure.
- Sunlight Exposure: Assess the amount of sunlight the roof receives throughout the day and choose plants that thrive in those conditions.
- Wind Exposure: Consider the wind conditions on the roof, as strong winds can damage plants.
- Maintenance Requirements: Choose plants that require minimal maintenance, especially for extensive green roofs.
- Aesthetics: Consider the desired aesthetic and choose plants that provide the desired look and feel.
Popular plant choices for green roofs include:
- Sedums: These succulents are drought-tolerant, low-maintenance, and come in a variety of colors and textures. They are a staple for extensive green roofs.
- Grasses: Ornamental grasses add texture and movement to the roof.
- Wildflowers: Wildflowers provide vibrant color and attract pollinators.
- Herbs: Herbs like thyme and oregano can be used in intensive green roofs for culinary purposes.
- Shrubs and Trees (Intensive Roofs): For intensive green roofs, consider dwarf shrubs and trees that are suitable for rooftop environments.
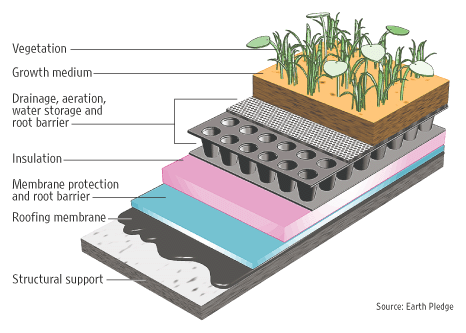
Substrate Composition: The Foundation for Growth
The substrate, also known as the growing medium, is the foundation upon which your plants will thrive. It provides the necessary nutrients, drainage, and aeration for healthy plant growth. The composition of the substrate is crucial and should be carefully considered.
Key components of a green roof substrate include:
- Mineral Components: Lightweight aggregates like lava rock, shale, or expanded clay provide drainage, aeration, and structural support.
- Organic Matter: Compost and other organic materials provide nutrients and improve water retention.
- pH Level: The substrate’s pH level should be appropriate for the selected plants, typically slightly acidic (around 6.0 to 7.0).
- Drainage Capacity: The substrate should have good drainage to prevent waterlogging and root rot.
The depth of the substrate varies depending on the type of green roof and the plants being grown. Extensive green roofs typically have a substrate depth of 2-6 inches, while intensive green roofs can have depths of 6 inches or more.
Drainage System: Preventing Waterlogging
Proper drainage is essential to prevent waterlogging, which can damage plants and the roofing membrane. A well-designed drainage system removes excess water from the substrate, ensuring healthy root growth.
Key components of a green roof drainage system include:
- Drainage Layer: This layer, typically made of a drainage mat or gravel, allows water to flow away from the substrate.
- Filter Fabric: This layer prevents soil particles from clogging the drainage layer.
- Drainage Outlets: These outlets allow water to drain off the roof.
Irrigation System: Ensuring Adequate Hydration
While some green roofs rely solely on rainfall, an irrigation system is often necessary, especially in drier climates. The irrigation system ensures that plants receive adequate water, particularly during establishment and periods of drought.
Common irrigation methods for green roofs include:
- Drip Irrigation: This method delivers water directly to the plant roots, minimizing water waste.
- Sprinkler Systems: These systems provide overhead watering, which can be suitable for certain plant types.
- Hand Watering: For smaller green roofs, hand watering can be a viable option.
Waterproofing Membrane: Protecting the Roof Structure
A high-quality waterproofing membrane is essential to protect the underlying roofing structure from water damage. The membrane should be durable, resistant to root penetration, and installed correctly to prevent leaks.
Installation: Bringing Your Green Roof to Life
Once the planning phase is complete, it’s time to install the green roof system. This process typically involves the following steps:
- Prepare the Roof Surface: Clean the roof surface and ensure it is free of debris.
- Install the Waterproofing Membrane: Apply the waterproofing membrane according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Install the Root Barrier (If Applicable): If using a membrane that is not root-resistant, install a root barrier to prevent root penetration.
- Install the Drainage Layer: Install the drainage layer, ensuring proper drainage.
- Install the Filter Fabric: Place the filter fabric over the drainage layer.
- Install the Substrate: Spread the substrate evenly across the roof.
- Plant the Vegetation: Plant the selected plants according to the planting plan.
- Install the Irrigation System (If Applicable): Install the irrigation system, ensuring proper coverage.
- Initial Watering: Water the newly planted vegetation thoroughly.
It’s highly recommended to hire experienced professionals for the installation process to ensure that the system is installed correctly and that the roof is watertight.
Maintenance: Nurturing Your Green Oasis
Regular maintenance is crucial to keep your green roof healthy and thriving. The maintenance requirements vary depending on the type of green roof and the plants being grown, but some general guidelines apply.
Watering
Watering is essential, especially during the establishment phase and periods of drought. Monitor the plants for signs of water stress, such as wilting or browning leaves, and adjust the watering schedule accordingly. Overwatering can be just as harmful as underwatering, so finding the right balance is key.
Fertilization
Fertilizing helps to replenish nutrients in the substrate, promoting healthy plant growth. Use a slow-release fertilizer specifically formulated for green roofs. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates.
Weeding
Weeds can compete with the desired plants for resources, so regular weeding is necessary. Remove weeds by hand or use a weed control fabric. Avoid using herbicides, as they can harm the plants and the environment.
Pruning
Pruning helps to maintain the shape and health of the plants. Prune plants as needed, removing dead or damaged growth. Pruning also encourages new growth and flowering.
Inspection
Regularly inspect the green roof for any signs of problems, such as leaks, drainage issues, or plant diseases. Address any issues promptly to prevent them from escalating.
Seasonal Care
Adapt your maintenance practices to the changing seasons. In the spring, fertilize and prune plants. In the summer, water more frequently. In the fall, remove any dead foliage and prepare the roof for winter. In the winter, monitor the roof for snow and ice buildup.
Troubleshooting Common Green Roof Issues
Even with the best planning and maintenance, problems can arise. Here’s how to address some common issues:
Poor Drainage
If water is not draining properly, it can lead to waterlogging and root rot. Check the drainage outlets for clogs and ensure that the drainage layer is functioning correctly. If necessary, repair or replace the drainage system.
Plant Diseases
Plant diseases can be caused by various factors, such as fungal infections or pests. Identify the disease and take appropriate action, such as removing infected plants or applying a fungicide. Ensure that the plants are receiving adequate sunlight and air circulation.
Weed Infestation
Weeds can quickly take over a green roof if not controlled. Remove weeds by hand or use a weed control fabric. Regular weeding is essential to prevent weed infestation.
Plant Die-Off
Plant die-off can be caused by various factors, such as poor drainage, insufficient watering, or plant diseases. Identify the cause of the die-off and take appropriate action, such as improving drainage, adjusting the watering schedule, or treating plant diseases.
Leaks
Leaks can damage the underlying roofing structure. Inspect the roof regularly for any signs of leaks. If a leak is detected, repair the waterproofing membrane promptly.
The Future of Green Roofs
Green roofs are more than just a trend; they represent a shift towards sustainable urban development. As cities become denser and the need for green spaces grows, green roofs will play an increasingly important role in creating healthier and more resilient urban environments. Innovations in green roof technology are constantly emerging, including:
- Modular Systems: These systems use pre-planted trays or modules that can be easily installed and replaced.
- Smart Irrigation: These systems use sensors to monitor soil moisture and automatically adjust irrigation schedules.
- Living Walls: Vertical green walls are another form of green infrastructure that can be integrated with green roofs.
- Biodiverse Green Roofs: Designing green roofs to support a variety of plant and animal life, creating ecosystems.
With continued research and development, the possibilities for green roofs are endless. They will continue to evolve, offering even greater environmental and aesthetic benefits.
Conclusion: Embracing the Green Revolution
Green roofs offer a compelling solution to many of the environmental challenges facing our cities. By understanding the planting specifications and following the guidelines outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can create a thriving rooftop ecosystem that enhances your property, benefits the environment, and provides a beautiful green space for you to enjoy. So, take the plunge, embrace the green revolution, and transform your roof into a vibrant oasis!
