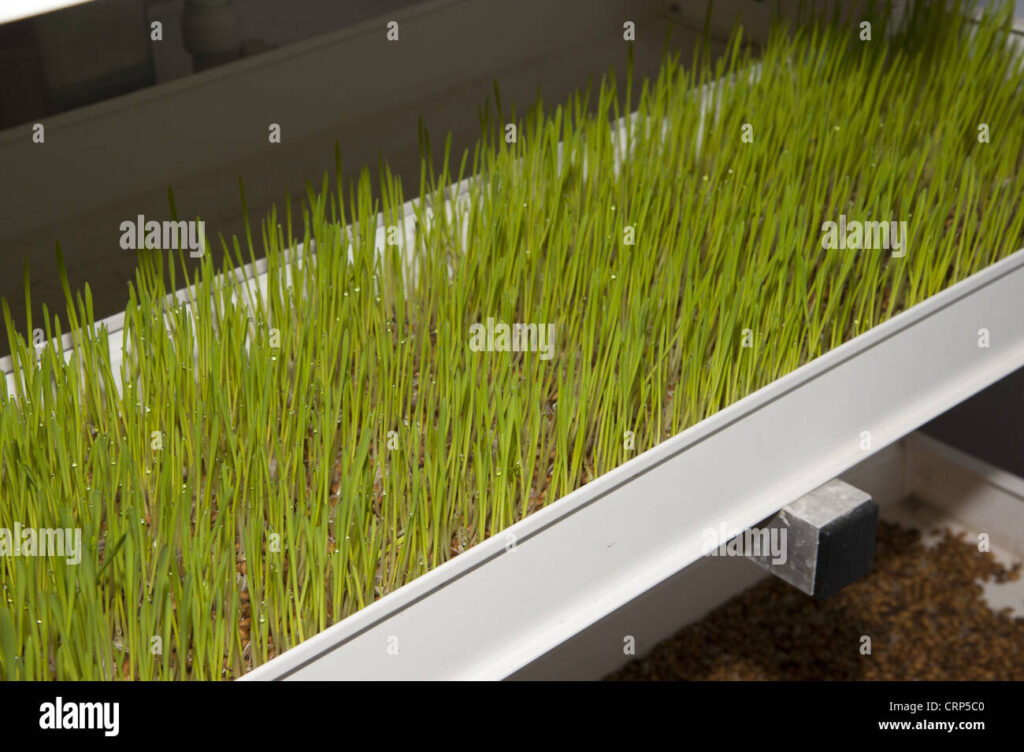
The world is changing, and with it, so is the way we think about food. As awareness of sustainability and healthy eating grows, the demand for organic produce, especially grains, is skyrocketing. But traditional farming methods, with their reliance on vast land areas, heavy machinery, and often, harmful chemicals, are facing increasing scrutiny. Enter hydroponics – a revolutionary approach to agriculture that offers a compelling solution. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of growing organic grains hydroponically, providing you with the knowledge and tools to embark on this exciting journey, whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a curious beginner.
Why Hydroponics? The Future of Grain Production
Hydroponics, at its core, is the art of growing plants without soil. Instead, the roots are submerged in a nutrient-rich water solution. This method offers a plethora of advantages over traditional soil-based farming, making it particularly appealing for organic grain production:
- Water Conservation: Hydroponic systems use significantly less water than conventional agriculture. Water is recirculated and reused, minimizing waste and making it ideal for arid or water-scarce regions.
- Increased Yields: Plants in hydroponic systems often grow faster and produce higher yields due to optimal nutrient availability and controlled environmental conditions.
- Reduced Pest and Disease Problems: The controlled environment of a hydroponic system minimizes exposure to pests and diseases, reducing or eliminating the need for pesticides and herbicides.
- Year-Round Production: Hydroponic systems can be operated indoors, allowing for year-round grain production regardless of the climate.
- Space Efficiency: Hydroponics can be implemented in vertical systems, maximizing space utilization and making it suitable for urban environments or small spaces.
- Organic Control: It’s much easier to control the inputs in a hydroponic system, allowing you to ensure your grains are truly organic. You have complete control over the nutrients the plants receive.
These advantages make hydroponics an attractive option for growing organic grains, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient food system. As the world grapples with climate change and the need for food security, hydroponics offers a promising path forward.
Understanding Organic Grains: The Foundation of a Healthy Diet
Before diving into the specifics of hydroponic cultivation, it’s essential to understand what constitutes organic grains. Organic grains are grown without the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). This means that the entire production process, from seed selection to harvest, adheres to strict organic standards.
The benefits of consuming organic grains are numerous:
- Nutrient Density: Organic grains often contain higher levels of essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Reduced Exposure to Harmful Chemicals: By avoiding synthetic pesticides and herbicides, organic grains minimize exposure to potentially harmful chemicals.
- Environmental Sustainability: Organic farming practices promote soil health, reduce water pollution, and support biodiversity.
- Improved Flavor and Taste: Many people find that organic grains have a richer, more complex flavor profile.
- Supports Sustainable Agriculture: Choosing organic grains supports farmers who prioritize environmental stewardship and sustainable practices.
Common organic grains that can be successfully grown hydroponically include:
- Wheat: A staple grain used in bread, pasta, and other baked goods.
- Barley: Used in brewing beer, making soups, and other culinary applications.
- Oats: A versatile grain used in oatmeal, granola, and other breakfast foods.
- Rye: Used in rye bread and other specialty products.
- Corn: Used in various foods, from tortillas to breakfast cereals.
The versatility of these grains makes them a great choice to start your hydroponic journey.
Setting Up Your Hydroponic System: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now, let’s get down to the practical aspects of growing organic grains hydroponically. The first step is setting up your system. There are several hydroponic systems that can be used, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The best system for you will depend on your space, budget, and experience level.
Choosing the Right System
Here are a few popular hydroponic systems suitable for growing grains:
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): This simple system involves suspending plant roots in a nutrient-rich water solution that is constantly aerated. It’s relatively inexpensive and easy to set up, making it a good option for beginners.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): In this system, a shallow stream of nutrient solution flows over the plant roots. It’s efficient and well-suited for larger-scale production.
- Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain): This system periodically floods the grow tray with nutrient solution and then drains it back into the reservoir. It’s relatively simple to build and maintain.
- Drip System: Nutrient solution is delivered to the plant roots via a drip line. This system is well-suited for larger operations.
For beginners, a DWC or Ebb and Flow system is often recommended due to their simplicity and ease of use. As you gain experience, you can explore more complex systems like NFT or drip systems.
Essential Components
Regardless of the system you choose, you’ll need the following essential components:
- Grow Tray or Container: This will hold your plants and the nutrient solution.
- Reservoir: This container holds the nutrient solution.
- Air Pump and Air Stone (for DWC): The air pump provides oxygen to the nutrient solution, which is essential for root health.
- Water Pump (for NFT, Ebb and Flow, and Drip Systems): The water pump circulates the nutrient solution.
- Grow Media: This provides support for the plant roots. Common options include rockwool, coco coir, perlite, and clay pebbles.
- Nutrient Solution: This provides the essential nutrients for plant growth. Choose a high-quality organic nutrient solution specifically formulated for hydroponics.
- pH and TDS Meter: These meters are used to monitor the pH and total dissolved solids (TDS) of the nutrient solution, which are crucial for plant health.
- Grow Lights: Since hydroponic systems can be operated indoors, you’ll need grow lights to provide the necessary light for photosynthesis. LED grow lights are an energy-efficient and effective option.
- Seeds: Choose high-quality organic grain seeds from a reputable supplier.
- Timer: A timer is used to control the operation of the water pump and grow lights.
Setting Up Your System: A Practical Guide
Here’s a general guide to setting up a basic DWC system:
- Assemble the system components: Gather all the necessary components, including the grow tray, reservoir, air pump, air stone, grow media, nutrient solution, pH meter, and TDS meter.
- Prepare the nutrient solution: Fill the reservoir with water and add the organic nutrient solution according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Adjust the pH to the recommended range (typically between 5.5 and 6.5).
- Plant the seeds: Soak your seeds for a few hours before planting. Place the seeds in the grow media, such as rockwool cubes or coco coir plugs.
- Position the plants in the grow tray: Place the grow media with the seedlings in the grow tray.
- Introduce the air stone and pump: Submerge the air stone in the nutrient solution and connect it to the air pump. The air pump will provide oxygen to the roots.
- Position the grow lights: Place the grow lights above the grow tray, ensuring they are at the appropriate distance from the plants.
- Monitor and adjust: Regularly monitor the pH and TDS of the nutrient solution and adjust as needed. Replenish the nutrient solution as necessary.
- Provide the necessary light: Ensure the plants receive the appropriate amount of light per day, depending on the grain type.
Remember to clean and sanitize all equipment before starting to prevent the spread of diseases.
Choosing the Right Grow Media
The grow media provides support for the plant roots and helps retain moisture and nutrients. Selecting the right grow media is crucial for the success of your hydroponic grain project. Here are some popular options:
- Rockwool: A popular choice for its excellent water retention and aeration properties. It’s made from spun basalt rock.
- Coco Coir: Made from coconut husks, coco coir is a sustainable and environmentally friendly option that offers good water retention and aeration.
- Perlite: A volcanic glass that improves drainage and aeration.
- Clay Pebbles: Inert, lightweight clay pellets that provide excellent drainage and aeration.
The best grow media for you will depend on the hydroponic system you choose and your personal preferences. Consider the water retention, drainage, and aeration properties of each option when making your decision.
Preparing the Nutrient Solution: The Lifeblood of Your Hydroponic Garden
The nutrient solution is the lifeblood of your hydroponic system, providing the essential nutrients that plants need to grow. Choosing the right organic nutrient solution and maintaining its pH and TDS levels is critical for the health and productivity of your plants.
Selecting an Organic Nutrient Solution
When choosing a nutrient solution, look for a high-quality organic formula specifically designed for hydroponics. These solutions are made from natural ingredients and provide a balanced blend of essential nutrients. Look for solutions that are certified organic to ensure they meet the highest standards. Some good options include:
- General Hydroponics Flora Series: A popular and versatile line of hydroponic nutrients.
- Botanicare Pure Blend Pro: Another popular line of hydroponic nutrients, known for its simplicity and effectiveness.
- Advanced Nutrients: A line of hydroponic nutrients with a focus on boosting yields.
Monitoring pH and TDS
Regularly monitoring the pH and TDS of your nutrient solution is essential for plant health. The pH measures the acidity or alkalinity of the solution, while TDS measures the concentration of dissolved solids. Use a pH meter and TDS meter to monitor these levels.
- pH: The ideal pH range for most hydroponic crops is between 5.5 and 6.5. Adjust the pH using pH up or pH down solutions as needed.
- TDS: The TDS level should be maintained within the recommended range for the specific crop. The recommended TDS level will depend on the grain type and the stage of growth.
Adjusting the pH and TDS levels ensures that the plants can effectively absorb nutrients.
Lighting Requirements for Hydroponic Grains
Light is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into food. In a hydroponic system, you’ll need to provide artificial lighting to supplement or replace natural sunlight. The type and intensity of light required will depend on the grain you’re growing and the stage of growth.
Types of Grow Lights
Several types of grow lights are available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- LED Grow Lights: Energy-efficient and long-lasting, LED grow lights are a popular choice for hydroponics. They come in various spectrums, allowing you to tailor the light to the specific needs of your plants.
- Fluorescent Grow Lights: Relatively inexpensive and energy-efficient, fluorescent grow lights are suitable for seedlings and vegetative growth.
- High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) Lights: Effective for flowering and fruiting, HPS lights produce a lot of heat and require a ballast.
- Metal Halide Lights: Provide a full spectrum of light, suitable for vegetative growth.
LED grow lights are generally considered the best option for hydroponic grain production due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and ability to provide a tailored light spectrum.
Light Schedules
The light schedule (the amount of time the plants are exposed to light) will depend on the grain type and the stage of growth. Generally, grains require 12-16 hours of light per day during the vegetative stage and 10-12 hours during the flowering stage. Research the specific light requirements for the grain you are growing.
Make sure to position the lights at the appropriate distance from the plants to prevent burning. Adjust the distance as the plants grow.
Germination and Seedling Care
Starting with healthy seedlings is crucial for the success of your hydroponic grain project. Germination is the process of a seed sprouting and developing into a seedling. Here’s how to ensure successful germination and seedling care:
Germination Methods
- Direct Sowing: Some grains can be directly sown into the grow media.
- Pre-Soaking: Soaking the seeds in water for a few hours before planting can improve germination rates.
- Paper Towel Method: Place the seeds on a damp paper towel, cover with another damp paper towel, and place in a warm location. Check the seeds daily for germination.
Once the seeds have germinated, transplant them into your hydroponic system.
Seedling Care
Provide the seedlings with:
- Proper Lighting: Use grow lights to provide the appropriate light spectrum and intensity.
- Optimal Temperature: Maintain a consistent temperature within the recommended range for the specific grain.
- Adequate Humidity: Maintain proper humidity levels for the seedling stage.
- Nutrient Solution: Start with a diluted nutrient solution and gradually increase the concentration as the seedlings grow.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly check the seedlings for signs of pests, diseases, and nutrient deficiencies.
Proper seedling care will set your plants up for success.
Growing and Harvesting Your Organic Grains
Once your seedlings are established, it’s time to focus on growing and harvesting your organic grains. This involves providing the right environmental conditions, nutrients, and care throughout the plant’s life cycle.
Growth Stages
The growth cycle of grains typically includes the following stages:
- Germination: The seed sprouts and develops into a seedling.
- Vegetative Growth: The plant grows leaves and stems.
- Flowering: The plant produces flowers.
- Grain Development: The grain develops within the flower.
- Ripening: The grain matures and is ready for harvest.
Each stage requires specific care and attention.
Nutrient Management
Adjust the nutrient solution concentration based on the plant’s growth stage. Monitor the pH and TDS levels regularly. Supplement with additional nutrients as needed.
Pest and Disease Control
Hydroponic systems are less susceptible to pests and diseases than soil-based systems. However, it’s still important to monitor your plants for any signs of infestation or disease. Use organic pest control methods if needed.
Harvesting
Harvest your grains when they are fully mature. The harvest time will vary depending on the grain type. Once harvested, dry the grains to prevent spoilage.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Even with the best care, you may encounter some challenges while growing organic grains hydroponically. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and other symptoms can indicate nutrient deficiencies. Adjust the nutrient solution and add supplements as needed.
- pH Imbalances: Improper pH levels can affect nutrient absorption. Regularly monitor and adjust the pH.
- Pest Infestations: Inspect your plants regularly for pests. Use organic pest control methods if necessary.
- Root Rot: Root rot can occur in systems with poor aeration. Ensure proper aeration and clean the system regularly.
- Algae Growth: Algae can grow in the nutrient solution if there is too much light. Cover the reservoir to prevent algae growth.
By understanding these potential problems, you can be prepared to address them and keep your hydroponic garden thriving.
The Future of Hydroponic Grain Production
The future of hydroponic grain production is bright. As the world faces challenges related to food security, climate change, and sustainable agriculture, hydroponics offers a promising solution. Innovations in hydroponic technology, such as vertical farming and automated systems, are making it even more efficient and accessible.
Hydroponics is not just a trend; it’s a paradigm shift in how we grow food. It provides a sustainable and efficient way to produce organic grains, contributing to a healthier planet and a more resilient food system.
Tips for Success and Resources
To ensure your success in growing organic grains hydroponically, consider the following tips:
- Start Small: Begin with a small-scale system and gradually expand as you gain experience.
- Research: Learn as much as you can about the specific grains you want to grow.
- Monitor Regularly: Regularly monitor the pH, TDS, and other environmental conditions.
- Be Patient: Growing grains hydroponically takes time and effort. Be patient and persistent.
- Connect with Others: Join online forums and communities to connect with other hydroponic growers and share your experiences.
Here are some valuable resources to help you on your hydroponic journey:
- Online Forums and Communities: Engage with other growers.
- Books and Guides: Read books and guides on hydroponics.
- Local Hydroponic Stores: Get advice and supplies.
- University Extension Programs: Attend workshops and training programs.
Embarking on the journey of growing organic grains hydroponically is a rewarding experience. It’s a way to connect with nature, contribute to a sustainable food system, and enjoy the satisfaction of harvesting your own fresh, healthy grains. Embrace the challenge, learn from your experiences, and enjoy the process. The future of food is in your hands.