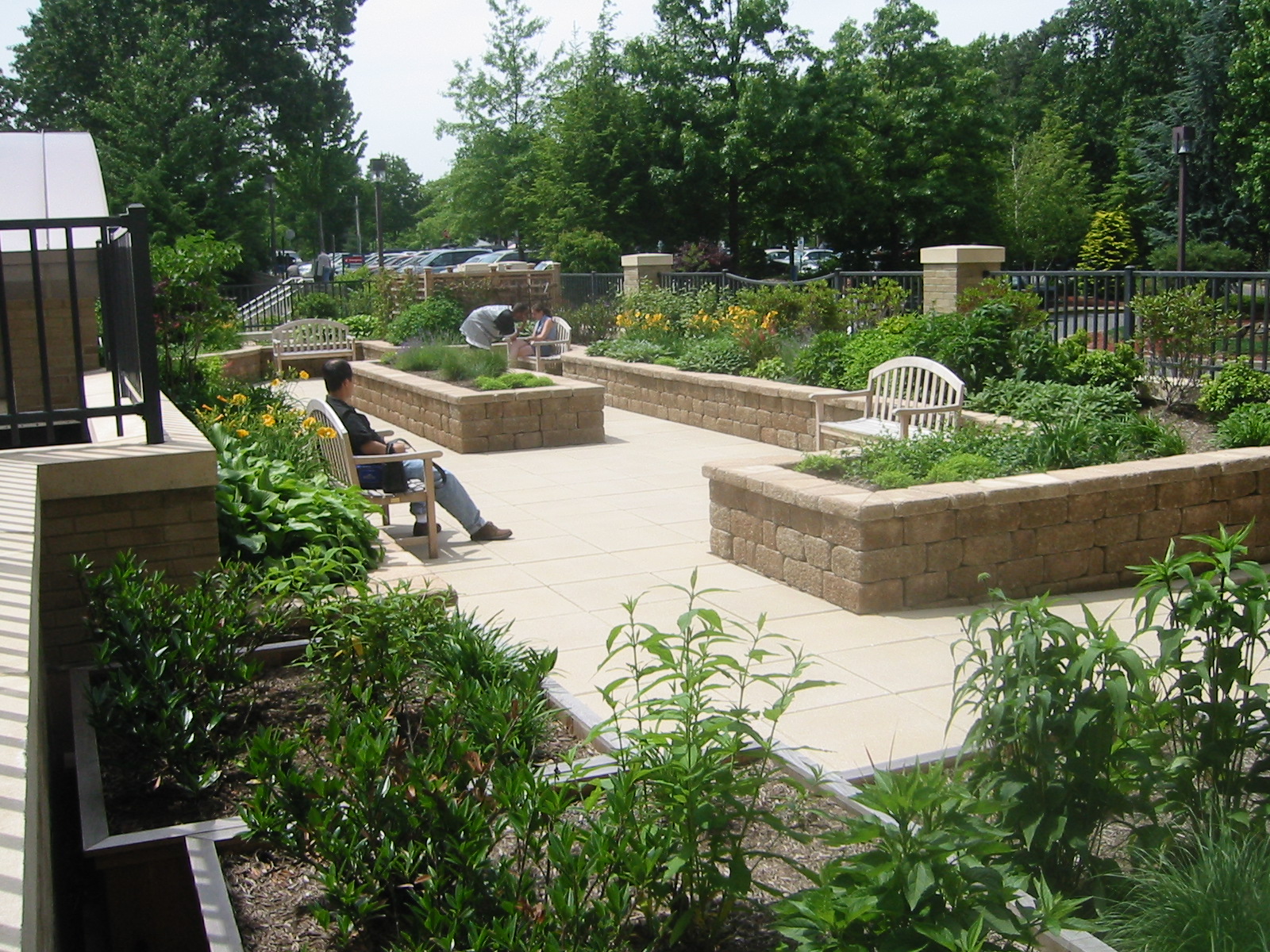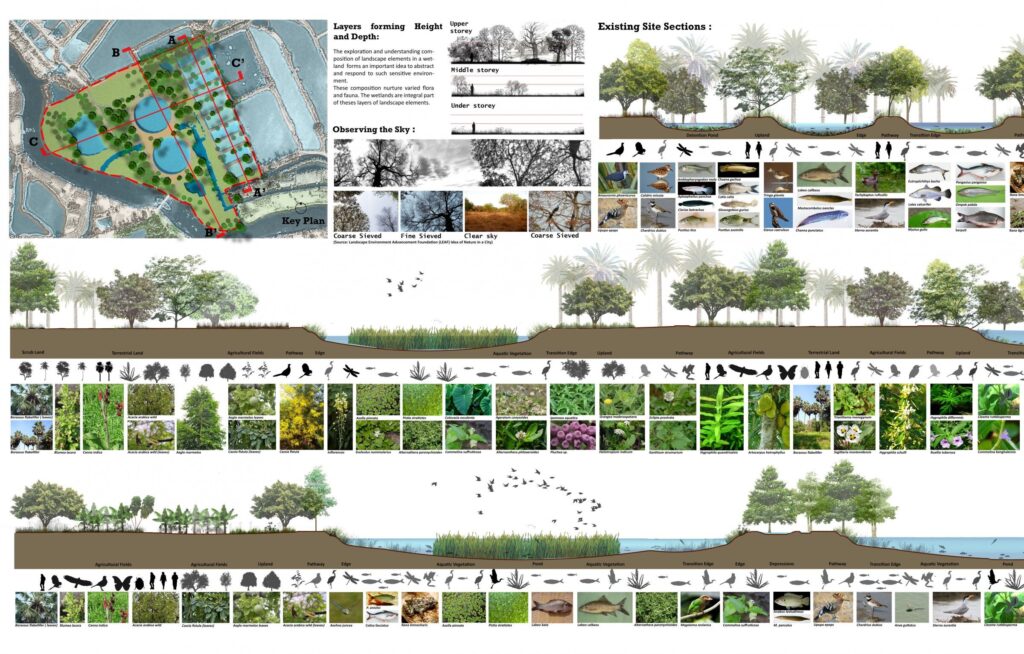
Introduction: Embracing Ecological Landscape Design
In an era where environmental consciousness is no longer a trend but a necessity, ecological landscape design emerges as a pivotal approach to harmonizing our living spaces with the natural world. It’s more than just planting trees and flowers; it’s about creating self-sustaining ecosystems that benefit both humans and the environment. This comprehensive guide delves into the principles, practices, and profound impacts of implementing ecological landscape design, offering a roadmap for creating landscapes that are not only beautiful but also ecologically sound.
Ecological landscape design goes beyond aesthetics. It’s a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of all living things within a landscape. It aims to minimize environmental impact, conserve resources, and enhance biodiversity. By understanding the local ecosystem and integrating its natural processes into the design, we can create landscapes that are resilient, sustainable, and beneficial to the planet.
Understanding the Core Principles
The foundation of ecological landscape design rests on several key principles, each playing a vital role in creating a balanced and thriving ecosystem:
1. Site Analysis: Knowing Your Land
Before any design can take shape, a thorough site analysis is crucial. This involves understanding the existing conditions of the land, including soil type, drainage patterns, sunlight exposure, wind patterns, and existing vegetation. It’s about becoming intimately familiar with the nuances of the site to make informed decisions that respect its natural characteristics. For example, understanding the soil composition helps in selecting plants that will thrive without excessive fertilization or irrigation. Identifying drainage patterns can prevent erosion and water waste. This initial assessment is the cornerstone of a successful ecological landscape design.
2. Native Plant Selection: Celebrating Local Flora
Choosing native plants is paramount in ecological landscape design. Native plants are adapted to the local climate, soil conditions, and wildlife, making them more resilient and requiring less maintenance than non-native species. They also provide essential food and habitat for native insects, birds, and other animals, contributing to biodiversity and a healthy ecosystem. Incorporating native plants is not just about aesthetics; it’s about fostering a sense of place and supporting the local ecology. Imagine a garden buzzing with native bees and butterflies, all thanks to the carefully selected native plants.
3. Water Conservation: Using Water Wisely
Water is a precious resource, and ecological landscape design prioritizes its conservation. Implementing water-wise strategies such as xeriscaping (designing landscapes that require little or no irrigation), rainwater harvesting, and efficient irrigation systems can significantly reduce water consumption. Grouping plants with similar water needs and using mulch to retain soil moisture are also effective techniques. The goal is to create a landscape that thrives with minimal reliance on external water sources, reducing both environmental impact and water bills.
4. Soil Health: Nurturing the Foundation
Healthy soil is the foundation of a healthy landscape. Ecological landscape design emphasizes building and maintaining soil health through practices such as composting, cover cropping, and avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Composting enriches the soil with organic matter, improving its structure, water retention, and nutrient content. Cover crops protect the soil from erosion, suppress weeds, and add nutrients. Avoiding synthetic chemicals prevents soil degradation and protects beneficial soil organisms. A healthy soil ecosystem supports plant growth and overall landscape health.
5. Wildlife Habitat: Creating a Sanctuary
Ecological landscape design aims to create habitats that support a diverse range of wildlife. This can be achieved by providing food sources, shelter, and nesting sites for birds, insects, and other animals. Planting trees, shrubs, and flowers that provide berries, seeds, and nectar attracts wildlife. Creating brush piles, rock gardens, and water features provides shelter and nesting opportunities. By considering the needs of wildlife, we can transform our landscapes into thriving ecosystems that support biodiversity and ecological balance. Envision a backyard teeming with life, where birds sing, butterflies flutter, and frogs croak – a testament to a successful ecological landscape.
6. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A Natural Approach
Instead of relying on harmful pesticides, ecological landscape design embraces Integrated Pest Management (IPM), a holistic approach to pest control that minimizes environmental impact. IPM involves identifying pests, monitoring their populations, and using a combination of natural methods to control them. This may include introducing beneficial insects, using traps, and employing cultural practices that promote plant health. By avoiding synthetic pesticides, we protect beneficial insects, pollinators, and other wildlife, creating a healthier and more balanced ecosystem.
7. Sustainable Materials: Choosing Responsibly
The materials used in landscape construction should be sustainable and environmentally friendly. This includes using recycled materials, locally sourced materials, and avoiding materials that require excessive energy to produce or transport. For example, using reclaimed wood for decking, gravel from local quarries for pathways, and natural stone for walls can reduce the environmental footprint of the landscape. Choosing sustainable materials is a crucial aspect of ecological landscape design, ensuring that the landscape is not only beautiful but also environmentally responsible.
Practical Steps for Implementing Ecological Landscape Design
Implementing ecological landscape design involves a series of practical steps, from initial planning to ongoing maintenance:
1. Assessment and Planning: Laying the Groundwork
The first step is to conduct a thorough assessment of the existing landscape and develop a comprehensive plan. This includes identifying the goals of the project, assessing the site conditions, and creating a design that integrates ecological principles. Consider the following questions: What are the desired outcomes of the landscape? What are the existing challenges and opportunities? How can ecological principles be integrated into the design to achieve the desired outcomes? A well-defined plan is essential for a successful ecological landscape project.
2. Soil Preparation: Building a Strong Foundation
Proper soil preparation is crucial for plant health and overall landscape success. This involves amending the soil with compost, organic matter, and other nutrients to improve its structure, water retention, and fertility. Soil testing can help determine the specific nutrient needs of the soil. Consider the following steps: Remove any existing turf or vegetation. Amend the soil with compost and other organic matter. Test the soil to determine its nutrient levels. Adjust the soil pH as needed. A healthy soil foundation is essential for thriving plants and a resilient landscape.
3. Plant Selection and Placement: Creating a Harmonious Ecosystem
Choosing the right plants and placing them appropriately is essential for creating a harmonious and thriving ecosystem. Select native plants that are adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. Group plants with similar water and sunlight needs. Consider the mature size of the plants and their impact on the surrounding environment. A well-planned plant selection and placement strategy can create a beautiful and ecologically sound landscape.
4. Water Management: Conserving a Precious Resource
Implementing water-wise strategies is crucial for conserving water and reducing environmental impact. This includes using efficient irrigation systems, collecting rainwater, and designing landscapes that require little or no irrigation. Consider the following strategies: Install a drip irrigation system. Collect rainwater in barrels or cisterns. Use mulch to retain soil moisture. Group plants with similar water needs. A well-designed water management system can significantly reduce water consumption and promote a sustainable landscape.
5. Pest and Disease Management: A Natural Approach
Managing pests and diseases naturally is essential for protecting the environment and promoting a healthy ecosystem. This involves using Integrated Pest Management (IPM) techniques, such as introducing beneficial insects, using traps, and employing cultural practices that promote plant health. Avoid synthetic pesticides and herbicides, which can harm beneficial insects, pollinators, and other wildlife. A natural approach to pest and disease management can create a healthier and more balanced landscape.
6. Maintenance and Monitoring: Ensuring Long-Term Success
Ongoing maintenance and monitoring are essential for ensuring the long-term success of an ecological landscape. This includes regular weeding, pruning, mulching, and monitoring for pests and diseases. Adjust the maintenance practices as needed to maintain the health and vitality of the landscape. Regular monitoring can help identify potential problems early on, allowing for timely intervention and preventing more serious issues. A well-maintained ecological landscape will thrive for years to come, providing numerous benefits to both humans and the environment.
Benefits of Implementing Ecological Landscape Design
The benefits of implementing ecological landscape design are numerous and far-reaching, impacting both the environment and the well-being of individuals:
1. Environmental Benefits: A Greener Planet
Ecological landscape design significantly reduces environmental impact by conserving water, reducing pollution, and enhancing biodiversity. By using native plants, we reduce the need for irrigation, fertilizers, and pesticides. By creating wildlife habitats, we support biodiversity and ecological balance. By using sustainable materials, we reduce the environmental footprint of the landscape. These practices contribute to a healthier and more sustainable planet.
2. Economic Benefits: Saving Money and Resources
Ecological landscape design can save money and resources by reducing water consumption, lowering maintenance costs, and increasing property value. Water-wise landscapes require less irrigation, saving on water bills. Native plants require less maintenance, reducing labor costs. A well-designed ecological landscape can increase property value, making it a worthwhile investment. These economic benefits make ecological landscape design a financially sound choice.
3. Social Benefits: Enhancing Quality of Life
Ecological landscape design enhances quality of life by providing aesthetically pleasing spaces, promoting physical and mental well-being, and fostering a sense of community. Beautiful landscapes provide a sense of peace and tranquility. Spending time in nature has been shown to reduce stress and improve mental health. Community gardens and shared green spaces foster a sense of community and social connection. These social benefits make ecological landscape design a valuable asset to any community.
4. Health Benefits: A Healthier Lifestyle
Ecological landscape design promotes a healthier lifestyle by providing opportunities for physical activity, reducing exposure to harmful chemicals, and improving air quality. Gardening and landscaping provide opportunities for physical activity, promoting cardiovascular health and overall fitness. Avoiding synthetic pesticides and herbicides reduces exposure to harmful chemicals, protecting human health. Trees and plants absorb pollutants and release oxygen, improving air quality and promoting respiratory health. These health benefits make ecological landscape design a valuable investment in personal well-being.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Success
Examining real-world examples of successful ecological landscape design projects can provide inspiration and practical insights:
1. The High Line, New York City: An Urban Oasis
The High Line is a transformed elevated railway line into a vibrant public park in New York City. It features native plants, sustainable materials, and innovative water management systems. The High Line has become a popular destination for locals and tourists alike, providing a green oasis in the heart of the city. This project demonstrates the potential of ecological landscape design to transform urban spaces and enhance quality of life.
2. Millennium Park, Chicago: A Cultural Landmark
Millennium Park is a world-renowned park in Chicago that features sustainable design elements, such as green roofs, permeable pavements, and rainwater harvesting systems. The park is a popular destination for cultural events and recreational activities, providing a vibrant public space for the community. Millennium Park demonstrates the potential of ecological landscape design to create sustainable and vibrant public spaces.
3. Eden Project, Cornwall, UK: A Global Showcase
The Eden Project is a botanical garden in Cornwall, UK, that showcases plants from around the world in a series of geodesic domes. The project features sustainable design elements, such as rainwater harvesting, renewable energy, and waste recycling systems. The Eden Project is a popular tourist destination and educational center, promoting environmental awareness and sustainable practices. This project demonstrates the potential of ecological landscape design to create educational and inspiring spaces.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementation
Implementing ecological landscape design can present certain challenges, but these can be overcome with careful planning and execution:
1. Initial Costs: Investing in the Future
The initial costs of ecological landscape design may be higher than conventional landscaping due to the use of sustainable materials and specialized expertise. However, the long-term benefits, such as reduced water consumption and lower maintenance costs, can offset these initial costs. Consider the investment in ecological landscape design as an investment in the future, providing long-term environmental, economic, and social benefits.
2. Maintenance Requirements: Adapting to Nature
Ecological landscapes may require different maintenance practices than conventional landscapes. Native plants may require less pruning and fertilization, but they may also require more weeding and monitoring for pests and diseases. Adapt the maintenance practices to the specific needs of the landscape and be prepared to adjust as needed. Regular monitoring and adaptive management are essential for maintaining a healthy and thriving ecological landscape.
3. Public Perception: Educating and Engaging
Some people may be unfamiliar with ecological landscape design and may have misconceptions about its aesthetics and functionality. Educate the public about the benefits of ecological landscape design and engage them in the planning and implementation process. Show them examples of successful ecological landscapes and explain how they contribute to a healthier and more sustainable environment. Public education and engagement are essential for promoting the adoption of ecological landscape design.
The Future of Ecological Landscape Design
The future of ecological landscape design is bright, with increasing awareness of the environmental and social benefits it offers. As more people recognize the importance of sustainability, ecological landscape design will become increasingly prevalent in residential, commercial, and public spaces. Technological advancements, such as smart irrigation systems and soil sensors, will further enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of ecological landscapes. The future of landscape design is undoubtedly ecological, promising a greener and more sustainable world for generations to come.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
Implementing ecological landscape design is not just a trend; it’s a responsibility. By embracing ecological principles and practices, we can create landscapes that are not only beautiful but also environmentally sound, economically viable, and socially beneficial. Let us all commit to creating landscapes that support biodiversity, conserve resources, and enhance the well-being of our communities. The time to act is now, and the future of our planet depends on it. Start small, learn as you go, and inspire others to join the movement towards ecological landscape design. Together, we can create a world where humans and nature thrive in harmony.
By adopting ecological landscape design, we contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future, ensuring that our landscapes not only beautify our surroundings but also support the health and well-being of our planet and its inhabitants. It’s a conscious choice, a commitment to stewardship, and a legacy we leave for generations to come. Let’s cultivate a world where every landscape tells a story of harmony, balance, and respect for nature.
