Introduction: Embracing a Pest-Free Garden the Natural Way
The joy of gardening is unparalleled. There’s something deeply satisfying about nurturing life, watching tiny seeds sprout into vibrant plants, and eventually harvesting the fruits (and vegetables!) of your labor. But, as any gardener knows, this idyllic picture isn’t always a walk in the park. Pests, those unwelcome guests, can quickly turn your green paradise into a battleground. Fear not, fellow gardeners! There’s a better way than resorting to harsh chemicals. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of organic pest control, providing you with the knowledge and tools to cultivate a thriving, pest-free garden – all while staying true to nature.
Chemical pesticides might seem like a quick fix, but they often come with a hefty price. They can harm beneficial insects, pollute the soil and water, and even pose risks to human health. Organic pest control, on the other hand, offers a sustainable and eco-friendly approach. It’s about working with nature, not against it. By understanding the intricate relationships within your garden ecosystem, you can create a balanced environment that naturally keeps pests at bay.
Understanding the Enemy: Common Garden Pests and Their Damage
Before you can effectively combat pests, you need to know your enemy. Here’s a rundown of some of the most common garden pests and the damage they inflict:
Aphids: The Sap-Sucking Saboteurs
Aphids are tiny, pear-shaped insects that come in various colors, including green, black, and red. They love to suck the sap from your plants, weakening them and causing stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and distorted stems. They also secrete a sticky substance called honeydew, which can attract ants and promote the growth of sooty mold.
Spider Mites: The Invisible Invaders
These microscopic pests are difficult to spot with the naked eye, but their damage is quite evident. Spider mites suck the sap from plant cells, causing stippling (tiny yellow or white spots) on the leaves. Severe infestations can lead to bronzing or browning of the foliage and even plant death. They thrive in hot, dry conditions.
Caterpillars: The Leaf-Munching Machines
Caterpillars, the larval stage of butterflies and moths, can devour entire plants in a matter of days. They come in various shapes, sizes, and colors, and they are voracious eaters. Look for chewed leaves, holes in foliage, and caterpillar droppings (frass) as signs of their presence.
Slugs and Snails: The Slimy Destroyers
These nocturnal pests love to feed on tender leaves, stems, and fruits. They leave behind telltale silvery slime trails. Slugs and snails are particularly active in damp, humid conditions.
Japanese Beetles: The Metallic Menace
These iridescent beetles are notorious for their destructive feeding habits. They skeletonize leaves, leaving behind only the veins, and they also feed on flowers and fruits. They are particularly fond of roses, grapes, and other ornamental plants.
Squash Bugs: The Squash Plant Assassins
Squash bugs are true pests in the squash garden. They feed on sap from squash plants, causing leaves to wilt and turn brown. They can also transmit diseases. These bugs are particularly tough to eradicate and can be a real pain for gardeners.
Whiteflies: The Tiny, Troublesome Flyers
Whiteflies are tiny, white, fly-like insects that suck sap from plants. They often congregate on the undersides of leaves. Like aphids, they also produce honeydew, which can lead to sooty mold. They can quickly multiply and spread through a garden.
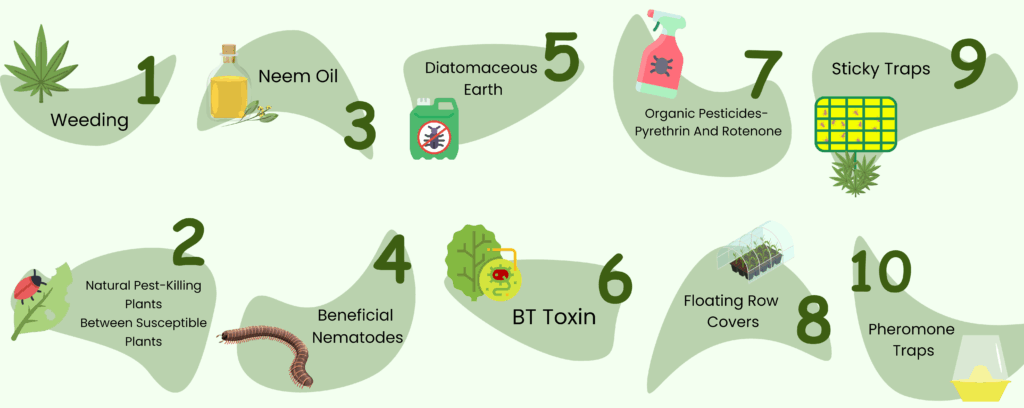
Organic Pest Control Strategies: A Multi-Faceted Approach
Organic pest control isn’t just about spraying a single product. It’s about creating a holistic approach that encompasses several strategies, working together to protect your plants. Here are some of the most effective methods:
1. Prevention is Key: Building a Resilient Garden
The best defense against pests is a strong offense. Prevention is the cornerstone of organic pest control. Here are some proactive measures you can take:
- Choose Resistant Varieties: Select plant varieties that are known to be resistant to common pests and diseases in your area. This is your first line of defense.
- Healthy Soil: Healthy soil is the foundation of a healthy garden. Amend your soil with compost, well-rotted manure, and other organic matter to improve its fertility, drainage, and overall structure. Healthy plants are more resilient to pests.
- Proper Watering: Water your plants at the base, avoiding overhead watering, which can create humid conditions that favor pests and diseases. Early morning watering is best, allowing foliage to dry before nightfall.
- Good Air Circulation: Space your plants adequately to allow for good air circulation. This helps to prevent fungal diseases and makes it more difficult for pests to find a home.
- Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests or diseases. Early detection is crucial for effective control.
- Cleanliness: Keep your garden clean by removing fallen leaves, weeds, and other debris, which can harbor pests and diseases.
2. Beneficial Insects: Nature’s Pest Control Army
One of the most exciting aspects of organic gardening is harnessing the power of beneficial insects. These natural predators and parasites can significantly reduce pest populations. Encourage these helpful critters by:
- Planting a Diverse Garden: A diverse garden provides a variety of food sources and habitats for beneficial insects. Include a mix of flowering plants, herbs, and vegetables.
- Providing Shelter: Create habitats for beneficial insects by leaving patches of unmowed grass, building insect hotels, or providing other sheltered areas.
- Avoiding Pesticides: Avoid using broad-spectrum pesticides, which can kill beneficial insects along with the pests you’re trying to control.
- Common Beneficial Insects: Some of the most effective beneficial insects include:
- Ladybugs: Voracious eaters of aphids and other soft-bodied insects.
- Lacewings: Their larvae, known as aphid lions, also feed on aphids and other pests.
- Praying Mantises: Generalist predators that eat a wide variety of insects.
- Parasitic Wasps: Lay their eggs inside the bodies of pests, eventually killing them.
- Minute Pirate Bugs: Tiny predators that feed on spider mites, thrips, and other small insects.
3. Manual Removal: The Hands-On Approach
Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the most effective. Manual removal involves physically removing pests from your plants. This can be a surprisingly effective method, especially for small infestations. Here’s how:
- Handpicking: Pick off larger pests, such as caterpillars, slugs, and Japanese beetles, by hand. Drop them into a bucket of soapy water to kill them.
- Pruning: Prune away infested leaves or stems to remove pests and prevent them from spreading.
- Water Spray: Use a strong jet of water from your hose to dislodge aphids, spider mites, and other small pests from your plants.
4. Organic Insecticides: Targeting Pests with Natural Solutions
When prevention and manual removal aren’t enough, organic insecticides can provide targeted control. These products are derived from natural sources and are generally safer for beneficial insects and the environment than synthetic pesticides. Here are some effective options:
- Insecticidal Soap: Effective against soft-bodied insects such as aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies. It works by disrupting the insect’s cell membranes.
- Horticultural Oil: Smothers insects and their eggs. Effective against aphids, spider mites, scale insects, and other pests.
- Neem Oil: Derived from the neem tree, neem oil has multiple uses. It acts as an insect repellent, disrupts insect growth, and can also control fungal diseases.
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): A naturally occurring bacterium that is toxic to certain caterpillars. It’s a very effective tool in the fight against leaf-munching caterpillars.
- Diatomaceous Earth (DE): A fine powder made from the fossilized remains of diatoms. It works by dehydrating insects. Use food-grade DE, and apply it carefully, as it can also harm beneficial insects.
5. Traps and Barriers: Preventing Pest Access
Traps and barriers can be effective in preventing pests from reaching your plants. Here are some options:
- Sticky Traps: Yellow sticky traps are effective for catching flying insects such as whiteflies, aphids, and fungus gnats.
- Slug Traps: Use beer traps (shallow dishes filled with beer) or other slug traps to attract and kill slugs and snails.
- Row Covers: Use floating row covers to protect plants from insect pests.
- Copper Tape: Wrap copper tape around the base of plants to deter slugs and snails.
- Barriers: Create physical barriers, such as collars around the stems of plants, to prevent pests from reaching them.
Specific Pest Control Solutions: Addressing Common Garden Challenges
Let’s look at how to tackle some of the most common garden pest problems:
Aphids:
- Control: Blast them off with a strong jet of water. Introduce ladybugs or lacewings. Spray with insecticidal soap or neem oil.
Spider Mites:
- Control: Increase humidity by misting plants. Spray with insecticidal soap or horticultural oil. Introduce predatory mites.
Caterpillars:
- Control: Handpick caterpillars. Spray with Bt.
Slugs and Snails:
- Control: Handpick slugs and snails. Use beer traps or other slug traps. Use copper tape.
Japanese Beetles:
- Control: Handpick beetles. Use Japanese beetle traps (though these can also attract beetles from neighboring areas).
Squash Bugs:
- Control: Handpick adults and eggs. Use row covers.
Whiteflies:
- Control: Introduce beneficial insects (e.g., parasitic wasps). Use yellow sticky traps. Spray with insecticidal soap or neem oil.
Creating a Thriving Organic Garden: Beyond Pest Control
Organic pest control is just one piece of the puzzle. To truly create a thriving garden, you need to consider other factors:
Soil Health: The Foundation of Success
As mentioned earlier, healthy soil is crucial. Regularly amend your soil with compost, well-rotted manure, and other organic matter. Consider conducting a soil test to determine your soil’s nutrient levels and pH. This will help you make informed decisions about fertilization and soil amendments.
Watering Wisely: Conserving Resources
Watering is essential, but it’s also important to conserve water. Water deeply but infrequently, encouraging plants to develop deep roots. Use drip irrigation or soaker hoses to deliver water directly to the roots, minimizing water loss through evaporation. Mulch around your plants to help retain moisture.
Choosing the Right Plants: Matching Plants to Your Environment
Select plants that are well-suited to your climate, soil conditions, and sunlight exposure. Native plants are often a good choice, as they are adapted to the local environment and are less likely to require intensive care.
Companion Planting: Nature’s Synergy
Companion planting involves planting different types of plants together to benefit each other. Some plants can repel pests, attract beneficial insects, or improve soil health. For example, planting basil near tomatoes can help repel tomato hornworms, while planting marigolds can deter nematodes.
Crop Rotation: Breaking Pest Cycles
Crop rotation involves changing the location of your crops each year. This helps to break the life cycles of pests and diseases that may be specific to certain plants. It can also improve soil health.
Common Questions About Organic Pest Control
Let’s address some frequently asked questions about organic pest control:
Is organic pest control as effective as chemical pesticides?
Organic pest control can be just as effective as chemical pesticides, especially when implemented as part of a comprehensive strategy. It may require a bit more patience and observation, but it is far more sustainable and beneficial in the long run. The key is to address the underlying causes of pest problems and to create a balanced ecosystem.
Are organic insecticides safe for pets and children?
Organic insecticides are generally safer than synthetic pesticides, but it’s still important to exercise caution. Always read and follow the label instructions carefully. Keep pets and children away from treated areas until the product has dried.
How long does it take to see results?
The time it takes to see results from organic pest control methods can vary depending on the severity of the infestation and the methods used. Some methods, such as handpicking or using a strong jet of water, can provide immediate results. Others, such as introducing beneficial insects, may take several weeks or months to have a noticeable impact. Be patient and persistent.
Can I make my own organic pest control solutions?
Yes, you can make some organic pest control solutions at home, such as insecticidal soap or garlic spray. However, it’s important to research the recipes carefully and to test the solution on a small area of your plants before applying it to the entire garden. Be cautious of using homemade solutions, as they may not be as effective or safe as commercially available products.
What are the benefits of organic pest control?
The benefits of organic pest control are numerous: It protects beneficial insects, pollinators, and other wildlife. It reduces the risk of human and pet exposure to harmful chemicals. It promotes healthy soil and a balanced ecosystem. It is a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to gardening.
Conclusion: Embracing the Beauty of a Pest-Free, Organic Garden
Organic pest control is a journey, not a destination. It requires a commitment to learning, observation, and a willingness to work with nature. By embracing these methods, you can create a beautiful, thriving garden that is both pest-free and environmentally friendly. Remember, patience and persistence are key. Enjoy the process, and celebrate the rewards of a garden that is alive with life, beauty, and the satisfaction of knowing you’re doing your part to protect our planet.


