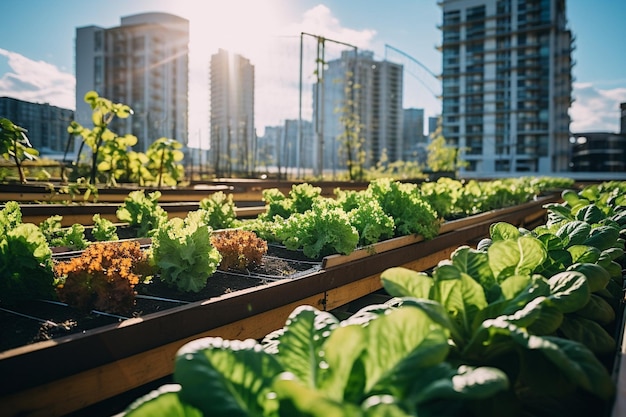
The concrete jungle, a term often used to describe our modern cities, is undergoing a quiet revolution. It’s a movement fueled by a desire for healthier lifestyles, environmental consciousness, and a reconnection with the origins of our food. This transformation is taking root in the most unexpected of places: our urban spaces. We’re witnessing a surge in sustainable urban farming initiatives, a trend that promises to reshape how we live, eat, and interact with our environment. This article will delve deep into the world of urban farming, exploring its diverse forms, the benefits it offers, the challenges it faces, and the innovative initiatives driving its growth.
What is Sustainable Urban Farming?
At its core, sustainable urban farming is the practice of growing food in urban environments using methods that minimize environmental impact and promote social equity. It’s a broad term that encompasses a wide range of practices, from small-scale rooftop gardens to larger community farms. The key element is sustainability, which means considering the long-term effects of our actions on the environment, the community, and the economy. This involves using resources efficiently, reducing waste, and fostering a sense of responsibility for our planet.
Unlike traditional agriculture, which often relies on pesticides, herbicides, and large-scale machinery, sustainable urban farming typically employs organic and environmentally friendly methods. This includes techniques like composting, rainwater harvesting, and integrated pest management. The focus is on creating a closed-loop system where resources are used efficiently and waste is minimized. It’s about producing food in a way that benefits both people and the planet.
The Diverse Forms of Urban Farming
Urban farming isn’t a one-size-fits-all concept. It takes on many forms, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Here are some of the most common:
- Rooftop Gardens: These gardens utilize the unused space on rooftops to grow a variety of crops. They can range from small-scale personal gardens to larger commercial operations. Rooftop gardens can help reduce building energy consumption, provide insulation, and manage stormwater runoff.
- Community Gardens: These are shared spaces where residents can come together to grow food. They often serve as a social hub, fostering a sense of community and providing educational opportunities. Community gardens can be found in vacant lots, parks, and other public spaces.
- Vertical Farming: This innovative approach involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often indoors. It uses technologies like hydroponics and aeroponics to maximize space and resource efficiency. Vertical farms can produce food year-round, regardless of weather conditions.
- Hydroponics and Aquaponics: These soilless growing methods use nutrient-rich water solutions to nourish plants. Hydroponics is often used in greenhouses and vertical farms, while aquaponics combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics, using the fish waste as fertilizer.
- Urban Orchards: These are public spaces planted with fruit trees and nut trees. They provide a source of fresh, local food and can also enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban areas.
- Indoor Farming: This encompasses a range of techniques, including growing crops in greenhouses, warehouses, and even repurposed buildings. Indoor farming allows for greater control over growing conditions, leading to higher yields and reduced reliance on pesticides.
The Benefits of Sustainable Urban Farming
The advantages of embracing sustainable urban farming are numerous and far-reaching, impacting not only the environment but also the health and well-being of urban communities. Here’s a closer look at some of the key benefits:
- Improved Access to Fresh, Healthy Food: Urban farms can provide residents with access to fresh, locally grown produce, especially in areas known as food deserts where access to grocery stores with fresh produce is limited. This can lead to improved nutrition and reduced rates of diet-related diseases.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: By growing food locally, urban farms reduce the need for long-distance transportation, which lowers carbon emissions and minimizes the environmental footprint associated with food production. They also promote sustainable practices like composting and water conservation.
- Waste Reduction: Urban farms can utilize food waste and organic matter through composting, turning waste into valuable resources for soil enrichment. This reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills.
- Community Building: Community gardens and urban farms often serve as social hubs, bringing people together to learn, share knowledge, and build relationships. They foster a sense of community and promote social cohesion.
- Educational Opportunities: Urban farms provide valuable educational opportunities for people of all ages. They can teach about sustainable food production, environmental stewardship, and healthy eating habits.
- Economic Benefits: Urban farms can create jobs, stimulate local economies, and provide opportunities for entrepreneurship. They can also reduce food costs and increase food security in urban areas.
- Improved Air Quality: Plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, helping to improve air quality in urban environments. Urban farms can also reduce the urban heat island effect by providing shade and cooling surfaces.
- Enhancing Biodiversity: Urban farms can create habitats for pollinators and other beneficial insects, contributing to biodiversity in urban areas. They can also provide green spaces that enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban environments.
Challenges Facing Urban Farming Initiatives
While the potential of sustainable urban farming is immense, it’s not without its challenges. These challenges need to be addressed in order to ensure the long-term success and sustainability of these initiatives:
- Land Availability and Cost: Finding suitable land for urban farms can be difficult and expensive, especially in densely populated areas. Competition for land with other uses, such as housing and commercial development, can be fierce.
- Access to Resources: Urban farms often face challenges in accessing resources such as water, electricity, and funding. Water scarcity, in particular, can be a significant constraint in some urban areas.
- Soil Contamination: Urban soils can be contaminated with pollutants from industrial activities, traffic, and other sources. This can pose a risk to food safety and human health.
- Pest and Disease Management: Managing pests and diseases in urban environments can be challenging. Urban farms need to employ integrated pest management strategies to minimize the use of pesticides and protect their crops.
- Lack of Knowledge and Expertise: Many urban farmers lack the knowledge and expertise needed to operate successful urban farms. Training and education programs are essential to address this gap.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Urban farms may face regulatory hurdles, such as zoning restrictions and permitting requirements. Streamlining these processes can help facilitate the growth of urban farming initiatives.
- Economic Viability: Ensuring the economic viability of urban farms can be challenging. They need to find ways to generate revenue, manage costs, and compete with conventional agriculture.
- Public Awareness and Support: Raising public awareness about the benefits of urban farming and garnering community support is crucial for the success of these initiatives.
Innovative Initiatives Shaping the Future of Urban Farming
Despite the challenges, the urban farming movement is thriving, fueled by innovative initiatives and technologies. Here are some examples of how cities and organizations are pushing the boundaries of urban agriculture:
- Vertical Farms: Companies like AeroFarms and Plenty are leading the way in vertical farming, using advanced technologies to grow crops indoors with minimal environmental impact. These farms can produce large quantities of food year-round, regardless of weather conditions.
- Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) Programs: CSAs connect farmers directly with consumers, providing a reliable market for locally grown produce. Members typically pay a fee upfront to receive a weekly share of the harvest throughout the growing season.
- Urban Agriculture Policy and Planning: Many cities are developing urban agriculture policies and plans to support the growth of urban farming. These policies can include zoning regulations, incentives for urban farmers, and funding for community gardens.
- Technology Integration: Technology is playing an increasingly important role in urban farming. This includes the use of sensors, drones, and data analytics to optimize growing conditions, monitor crop health, and improve efficiency.
- Food Waste Recycling Programs: Cities and organizations are implementing food waste recycling programs to divert organic waste from landfills and provide valuable compost for urban farms.
- Educational Programs and Workshops: Numerous educational programs and workshops are being offered to teach people about urban farming techniques, sustainable food production, and healthy eating habits.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaboration between urban farmers, community organizations, government agencies, and private companies is essential for the success of urban farming initiatives. These partnerships can help address challenges, share resources, and expand the reach of these programs.
- Funding and Investment: Increasing access to funding and investment is crucial for the growth of urban farming. This includes grants, loans, and crowdfunding opportunities for urban farmers and startups.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Urban Farming
Technology is proving to be a game-changer in the world of sustainable urban farming. It’s enabling farmers to overcome challenges, optimize resource use, and increase yields. Here’s how technology is transforming urban agriculture:
- Precision Agriculture: Sensors and data analytics are used to monitor growing conditions, such as soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. This information allows farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, leading to more efficient resource use and higher yields.
- Vertical Farming Technologies: Vertical farms rely heavily on technology to create optimal growing environments. This includes LED lighting, hydroponics, and aeroponics systems that provide plants with the nutrients and light they need to thrive.
- Drones: Drones can be used to monitor crop health, detect pests and diseases, and assess irrigation needs. They can also be used to map farm layouts and track yields.
- Automation: Automation is being used to streamline various farming tasks, such as planting, harvesting, and packaging. This helps reduce labor costs and improve efficiency.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices, such as smart sensors and connected irrigation systems, allow farmers to remotely monitor and control their operations. This can save time, reduce waste, and improve productivity.
- Data Analysis: Data analysis is used to track crop performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. This helps farmers optimize their operations and improve their bottom line.
The Future of Food: Embracing Sustainable Urban Farming
Sustainable urban farming is more than just a trend; it’s a vital part of building a more resilient and sustainable food system. By growing food locally, we can reduce our environmental impact, improve food security, and create healthier communities. As the world’s population continues to grow and urbanization increases, urban farming will play an even more critical role in meeting the food needs of future generations.
The initiatives and advancements we’re seeing today are just the beginning. With continued innovation, collaboration, and public support, urban farming has the potential to revolutionize how we produce and consume food. It’s a movement that empowers individuals, strengthens communities, and protects the planet. It’s a chance to reconnect with nature, learn new skills, and build a more sustainable future for all.
The future of food is being cultivated in our cities. By embracing sustainable urban farming, we’re not just growing food; we’re growing a better world.
How to Get Involved in Sustainable Urban Farming
Are you inspired to get involved in the urban farming movement? Here are some ways you can contribute:
- Start Your Own Garden: Even a small balcony garden or a few containers on a windowsill can make a difference. Grow herbs, vegetables, or fruits that you enjoy eating.
- Join a Community Garden: Find a community garden in your area and volunteer your time or rent a plot. This is a great way to learn about urban farming and connect with other gardeners.
- Support Local Farmers: Buy your produce from local farmers markets, CSAs, or urban farms. This supports local food production and reduces your environmental impact.
- Educate Yourself: Learn more about sustainable urban farming by reading books, attending workshops, or taking online courses.
- Advocate for Change: Support policies and initiatives that promote urban farming in your community. Contact your local government representatives and let them know you support urban agriculture.
- Volunteer Your Time: Offer your time and skills to help urban farms and community gardens.
- Donate: Support organizations that promote urban farming with financial donations.
- Spread the Word: Share your knowledge and enthusiasm for urban farming with your friends, family, and neighbors.
The journey towards a more sustainable and food-secure future starts with each one of us. By embracing sustainable urban farming, we can all contribute to building a healthier, more vibrant, and resilient world.