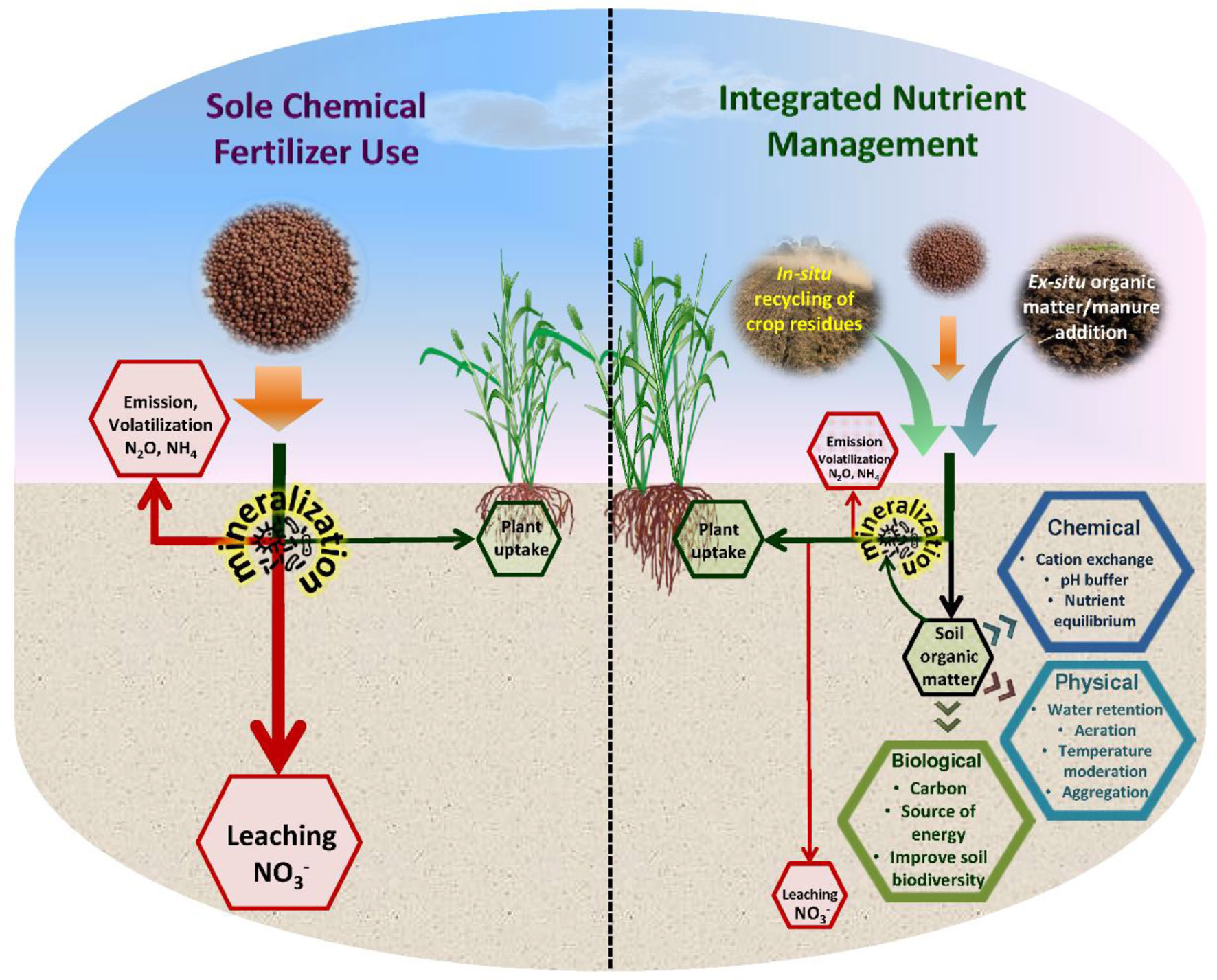
Revolutionizing Agriculture: Implementing Smart Fertilizer Delivery for Sustainable Farming
The world is changing, and with it, so is the way we approach food production. The demand for food is constantly increasing, driven by a growing global population and evolving dietary preferences. This, in turn, places immense pressure on agricultural practices to become more efficient, productive, and sustainable. At the heart of this transformation lies the need for smarter, more precise methods of farming, and one of the most critical aspects is fertilizer management. Implementing smart fertilizer delivery is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for ensuring food security, protecting the environment, and fostering a more resilient agricultural sector.
The Challenges of Traditional Fertilizer Application
Traditional fertilizer application methods often fall short in terms of efficiency and environmental impact. Farmers have historically relied on broad-spectrum applications, where fertilizers are spread uniformly across entire fields. While this approach may seem simple, it has several significant drawbacks:
- Over-fertilization: It’s easy to apply too much fertilizer, leading to nutrient runoff and environmental pollution.
- Under-fertilization: Inconsistent distribution can result in some areas receiving insufficient nutrients, hindering crop growth.
- Nutrient Runoff: Excess fertilizer can seep into waterways, causing eutrophication and harming aquatic ecosystems.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The production and use of fertilizers contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change.
- Economic Waste: Over-application wastes valuable resources and reduces farmers’ profitability.
These challenges highlight the need for a more targeted and precise approach to fertilizer delivery. Smart fertilizer delivery systems offer a solution by optimizing fertilizer application based on the specific needs of the crops and the conditions of the field.
The Principles of Smart Fertilizer Delivery
Smart fertilizer delivery systems are based on several key principles:
- Precision: Applying the right amount of fertilizer at the right time and in the right place.
- Data-Driven: Utilizing data from various sources, such as soil sensors, weather data, and crop monitoring, to make informed decisions.
- Variable Rate Application (VRA): Adjusting fertilizer application rates across different zones within a field based on specific needs.
- Sustainability: Minimizing environmental impact by reducing nutrient runoff and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Efficiency: Improving crop yields and reducing fertilizer waste.
By embracing these principles, smart fertilizer delivery systems can transform the way we manage nutrients in agriculture.
Technologies Driving Smart Fertilizer Delivery
Several technologies are crucial in enabling smart fertilizer delivery:
1. Soil Sensors
Soil sensors play a vital role in monitoring soil conditions. They provide real-time data on nutrient levels, moisture content, pH, and other critical parameters. This information allows farmers to make informed decisions about fertilizer application. There are different types of soil sensors available:
- Electromagnetic (EM) sensors: Measure soil electrical conductivity to assess soil properties, including nutrient content and salinity.
- Capacitance sensors: Measure soil moisture content by assessing the dielectric constant of the soil.
- Nitrate sensors: Detect nitrate levels in the soil, which is crucial for determining nitrogen fertilizer needs.
The data collected by soil sensors is used to create detailed soil maps, which can be used to guide variable rate application.
2. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and GPS
GIS and GPS technologies are essential for mapping fields and applying fertilizers precisely. GIS software allows farmers to visualize soil data, identify areas with specific nutrient deficiencies, and create application maps. GPS technology enables accurate navigation and variable rate application of fertilizers across the field. Combining GIS and GPS allows for the creation of precise application zones.
3. Remote Sensing and Drones
Remote sensing technologies, such as satellite imagery and drones, provide valuable data on crop health and growth. Drones equipped with multispectral cameras can capture images that reveal variations in plant health, nutrient deficiencies, and stress levels. This information helps farmers identify areas that need more or less fertilizer. The data can also be used to predict potential yield and optimize fertilizer application.
4. Variable Rate Applicators
Variable rate applicators are the machines that apply fertilizers at varying rates across the field. They are equipped with GPS receivers and are controlled by application maps generated from soil data, remote sensing data, and other sources. This technology ensures that fertilizer is applied only where and when it is needed, reducing waste and maximizing efficiency.
5. Weather Data and Forecasting
Weather data and forecasting tools provide valuable information about rainfall, temperature, and other environmental factors that affect fertilizer application. Farmers can use this information to adjust application schedules and rates to minimize nutrient runoff and maximize fertilizer effectiveness.
Benefits of Implementing Smart Fertilizer Delivery
The benefits of implementing smart fertilizer delivery are numerous and far-reaching:
1. Increased Crop Yields
By applying the right amount of fertilizer at the right time and place, smart fertilizer delivery systems optimize nutrient uptake and promote healthy crop growth. This leads to increased yields and higher profitability for farmers.
2. Reduced Fertilizer Costs
Variable rate application and precision fertilizer management reduce fertilizer waste by applying only what is needed. This can result in significant cost savings for farmers.
3. Improved Environmental Sustainability
Smart fertilizer delivery systems minimize nutrient runoff and reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with fertilizer use. This helps protect water quality and mitigate climate change.
4. Enhanced Nutrient Use Efficiency
Precision application ensures that crops can efficiently utilize the applied nutrients, reducing nutrient losses and improving overall efficiency.
5. Improved Crop Quality
Optimal nutrient management promotes healthier crops, which can lead to improved crop quality and higher market value.
6. Data-Driven Decision Making
Smart fertilizer delivery systems provide valuable data on soil conditions, crop health, and fertilizer application. This data can be used to make informed decisions about future fertilizer applications and improve overall farm management practices.
Steps to Implement Smart Fertilizer Delivery
Implementing smart fertilizer delivery involves several steps:
1. Assess Your Needs
Evaluate your current fertilizer application practices, identify areas for improvement, and determine your goals for adopting smart fertilizer delivery. Consider your crop types, soil conditions, and existing equipment.
2. Collect Data
Gather data on your soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns. This may involve soil testing, remote sensing, and weather monitoring.
3. Choose the Right Technologies
Select the technologies that best fit your needs and budget. Consider soil sensors, GIS and GPS, variable rate applicators, and other relevant tools.
4. Develop Application Maps
Create application maps based on the data you have collected. These maps will guide the variable rate application of fertilizers.
5. Calibrate Your Equipment
Calibrate your variable rate applicators and other equipment to ensure accurate fertilizer application.
6. Implement and Monitor
Implement your smart fertilizer delivery system and monitor its performance. Track crop yields, fertilizer use, and environmental impact to evaluate the effectiveness of your system.
7. Optimize and Refine
Continuously optimize and refine your system based on the data you collect and the results you achieve. Adapt your practices as needed to maximize efficiency and sustainability.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Smart Fertilizer Delivery
The benefits of smart fertilizer delivery are not just theoretical; they are being realized by farmers around the world. Here are a few examples:
1. Corn Production in the Midwest
Farmers in the Midwestern United States have adopted smart fertilizer delivery systems to optimize nitrogen application in corn production. By using soil sensors and variable rate applicators, they have reduced nitrogen fertilizer use by 15-20% while maintaining or even increasing crop yields. This has resulted in significant cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
2. Cotton Farming in Australia
Australian cotton farmers are using precision agriculture techniques, including smart fertilizer delivery, to improve water use efficiency and reduce fertilizer runoff. By applying fertilizers only where needed, they have decreased their environmental footprint and increased their profitability.
3. Wheat Farming in Europe
European wheat farmers are leveraging precision farming technologies to address the challenges of variable soil conditions and nutrient deficiencies. Through the use of soil mapping and variable rate fertilizer application, they have improved wheat yields and reduced fertilizer waste.
These case studies demonstrate the real-world benefits of smart fertilizer delivery and its potential to transform agriculture.
Challenges and Considerations
While smart fertilizer delivery offers significant advantages, there are also challenges and considerations to address:
- Initial Investment: Implementing smart fertilizer delivery systems can require a significant upfront investment in equipment and technology.
- Technical Expertise: Farmers may need to develop new skills and expertise to operate and maintain smart fertilizer delivery systems.
- Data Management: Managing and interpreting the data generated by these systems can be complex.
- Compatibility Issues: Ensuring compatibility between different technologies and systems can be challenging.
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting the privacy and security of the data collected by these systems is essential.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of smart fertilizer delivery often outweigh the costs. Careful planning and implementation can help farmers overcome these obstacles and achieve the desired results.
The Future of Smart Fertilizer Delivery
The future of smart fertilizer delivery is bright. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and efficient systems emerge. Here are some trends to watch:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms will be used to analyze data, predict crop needs, and optimize fertilizer application in real-time.
- Robotics and Automation: Robots and automated systems will be used to apply fertilizers, monitor crops, and collect data.
- Integration with Other Technologies: Smart fertilizer delivery systems will be integrated with other precision agriculture technologies, such as irrigation and pest management systems.
- Advanced Sensors: New sensors will be developed to provide more detailed information about soil conditions and crop health.
- Digital Platforms: Digital platforms will be used to manage data, share information, and connect farmers with experts and service providers.
These advancements will further enhance the efficiency, sustainability, and profitability of agriculture. Smart fertilizer delivery is poised to play a central role in the future of food production.
Conclusion: Embracing the Precision Revolution
Implementing smart fertilizer delivery is a crucial step toward building a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system. By embracing precision agriculture techniques, farmers can optimize fertilizer application, reduce environmental impact, and increase crop yields. While there are challenges to overcome, the benefits of smart fertilizer delivery are undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative solutions to emerge, further transforming the way we grow food. Now is the time for farmers, researchers, and policymakers to collaborate and embrace the precision revolution, paving the way for a more sustainable and food-secure future for all.