Buzzing Cities: Inviting Native Pollinators to Urban Havens
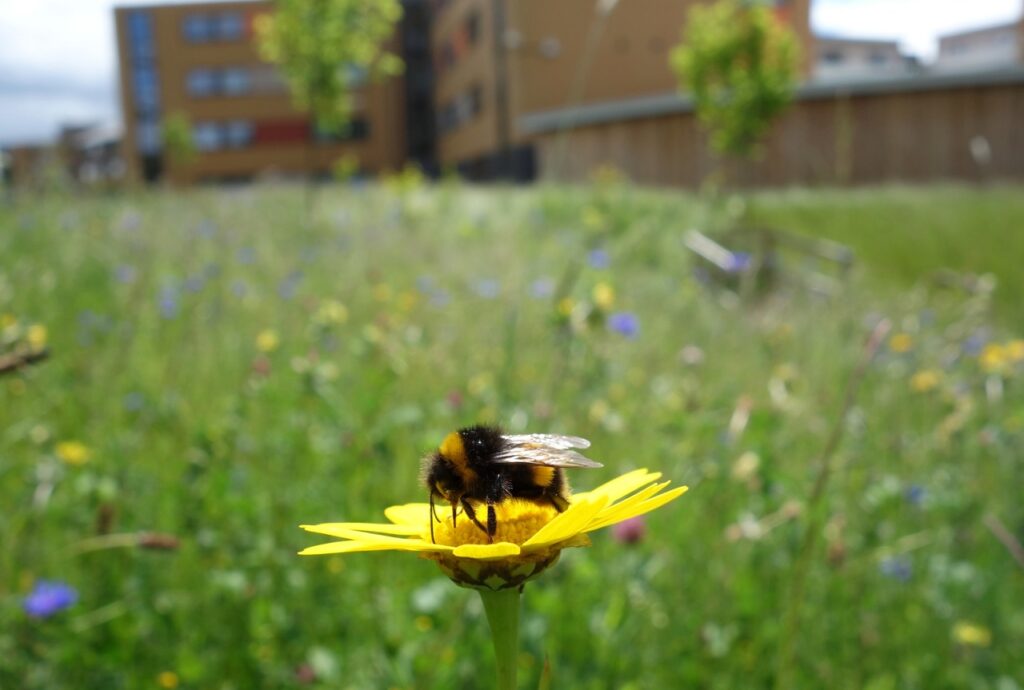
Our cities, often perceived as concrete jungles, can become vibrant ecosystems teeming with life. One of the most crucial aspects of urban biodiversity is the presence of native pollinators. These unsung heroes—bees, butterflies, moths, beetles, and even some birds and bats—play an indispensable role in maintaining the health and vitality of our urban environments and the broader planet. Attracting native pollinators to urban areas isn’t just a feel-good initiative; it’s a necessity for ecological balance, food security, and overall environmental sustainability.
But why are pollinators so important, and why are they in decline? The answer lies in the intricate web of life. Pollinators facilitate the reproduction of countless plant species, including many of the fruits, vegetables, and nuts we rely on for food. Without them, our food supply would be drastically diminished, and ecosystems would suffer severe consequences. Unfortunately, pollinator populations are facing unprecedented challenges due to habitat loss, pesticide use, climate change, and disease. Urban areas, despite their challenges, can provide vital refuges for these creatures if we take the right steps.</p
This comprehensive guide explores the myriad ways we can transform our cities into pollinator-friendly havens, from creating pollinator gardens to advocating for policy changes. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener, a city planner, or simply someone who cares about the environment, there’s something you can do to help.
Understanding the Importance of Native Pollinators
Before diving into the how-to, let’s take a closer look at why native pollinators are so crucial. Unlike honeybees, which are often imported and managed, native pollinators are adapted to local climates and ecosystems. They have evolved alongside native plants, forming intricate relationships that benefit both parties. For example, certain bee species have specialized mouthparts that allow them to pollinate specific types of flowers, while some plants rely exclusively on particular pollinators for reproduction.</p
The decline of native pollinators has far-reaching consequences. Beyond the obvious impact on agriculture, it can lead to a loss of biodiversity, reduced ecosystem resilience, and even economic instability. When pollinator populations dwindle, plant communities suffer, which in turn affects the animals that depend on those plants for food and shelter. This cascading effect can disrupt entire ecosystems, making them more vulnerable to environmental stressors.</p
Consider the monarch butterfly, an iconic North American pollinator. Monarch populations have plummeted in recent decades due to habitat loss and the decline of milkweed, the only plant on which monarch caterpillars can feed. This decline not only threatens the monarch butterfly itself but also has ripple effects throughout the ecosystems it inhabits.
The Economic Impact of Pollinator Decline
The economic impact of pollinator decline is staggering. According to some estimates, pollinators contribute billions of dollars to the global economy each year through their pollination services. Without them, farmers would have to rely on costly and less efficient methods of pollination, such as hand-pollination, which would drive up food prices and reduce agricultural productivity. Moreover, the loss of pollinators can negatively impact industries such as tourism and recreation, which rely on healthy ecosystems and vibrant landscapes.
Creating Pollinator-Friendly Habitats in Urban Areas
One of the most effective ways to attract native pollinators to urban areas is to create pollinator-friendly habitats. This involves planting a variety of native plants that provide food and shelter for pollinators throughout the growing season. Here are some key considerations:
Choosing the Right Plants
Selecting the right plants is crucial for attracting native pollinators. Native plants are adapted to local climates and soil conditions, making them easier to grow and more beneficial to pollinators. When choosing plants, consider the following factors:
- Bloom Time: Select plants that bloom at different times of the year to provide a continuous source of food for pollinators.
- Flower Shape and Color: Different pollinators are attracted to different flower shapes and colors. For example, bees are often attracted to blue, purple, and yellow flowers with shallow shapes, while butterflies prefer brightly colored flowers with landing platforms.
- Plant Diversity: Plant a variety of species to support a diverse range of pollinators.
- Native vs. Non-Native: Prioritize native plants over non-native species, as they are more likely to support local pollinator populations.
Some excellent native plants for attracting pollinators include:
- Bees: Bee balm, coneflower, lavender, salvia
- Butterflies: Milkweed, butterfly bush, aster, zinnia
- Hummingbirds: Salvia, trumpet vine, bee balm, honeysuckle
Designing Your Pollinator Garden
When designing your pollinator garden, consider the following tips:
- Sunlight: Most pollinator plants require at least six hours of sunlight per day.
- Soil: Choose well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter.
- Water: Provide a source of water for pollinators, such as a shallow dish of water with pebbles for them to land on.
- Shelter: Provide shelter for pollinators by planting shrubs and trees, or by creating brush piles or rock piles.
- Avoid Pesticides: Pesticides can be harmful to pollinators, so avoid using them in your garden.
Transforming Unused Spaces
Urban areas often have underutilized spaces that can be transformed into pollinator-friendly habitats. Vacant lots, rooftops, and even small balconies can be turned into thriving pollinator gardens. Consider these options:
- Rooftop Gardens: Rooftop gardens can provide valuable habitat for pollinators in urban areas where ground space is limited.
- Vertical Gardens: Vertical gardens are a great way to add greenery to small spaces and attract pollinators.
- Community Gardens: Community gardens can provide a shared space for residents to grow food and create pollinator-friendly habitats.
Reducing Pesticide Use in Urban Areas
Pesticides are a major threat to pollinator populations. Even pesticides that are not directly toxic to pollinators can have sublethal effects, such as impairing their ability to navigate or forage for food. Reducing pesticide use in urban areas is essential for protecting pollinators.
Alternatives to Pesticides
There are many alternatives to pesticides that can be used to control pests in urban areas. These include:
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): IPM is a holistic approach to pest control that emphasizes prevention and uses pesticides only as a last resort.
- Biological Control: Biological control involves using natural enemies of pests, such as beneficial insects, to control their populations.
- Cultural Practices: Cultural practices, such as crop rotation and proper sanitation, can help to prevent pest problems.
- Hand-Picking: Hand-picking pests off of plants can be an effective way to control small infestations.
Advocating for Policy Changes
Advocating for policy changes is another important way to reduce pesticide use in urban areas. This can involve working with local governments to ban or restrict the use of certain pesticides, or supporting legislation that promotes IPM practices.
Providing Water Sources for Pollinators
Like all living things, pollinators need water to survive. Providing a source of water for pollinators in urban areas can help to support their populations. Here are some simple ways to provide water for pollinators:
- Shallow Dishes: Place shallow dishes of water with pebbles or marbles in your garden. The pebbles provide a place for pollinators to land and drink without drowning.
- Bird Baths: Bird baths can also be used to provide water for pollinators, but make sure to keep the water shallow.
- Dripping Hoses: A dripping hose can provide a constant source of water for pollinators.
Creating Nesting Sites for Pollinators
Many native pollinators, such as bees and wasps, nest in the ground or in cavities in wood. Providing nesting sites for these pollinators can help to support their populations. Here are some ways to create nesting sites for pollinators:
Ground-Nesting Bees
About 70% of native bees nest in the ground. To create nesting sites for ground-nesting bees, leave patches of bare soil in your garden. Avoid tilling or disturbing these areas, as this can destroy bee nests.
Cavity-Nesting Bees
Cavity-nesting bees nest in holes in wood, stems, or other materials. To create nesting sites for cavity-nesting bees, you can build or purchase bee houses. Bee houses are typically made of wood and have holes of various sizes drilled into them. These holes provide nesting sites for different species of bees.
Brush Piles and Rock Piles
Brush piles and rock piles can provide shelter and nesting sites for a variety of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and moths.
Educating the Community
Educating the community about the importance of pollinators is essential for promoting pollinator conservation. This can involve hosting workshops, giving presentations, or simply talking to your neighbors about the importance of pollinators.
Community Outreach Programs
Community outreach programs can be a great way to educate the public about pollinators. These programs can involve:
- Workshops: Hosting workshops on how to create pollinator-friendly gardens.
- Presentations: Giving presentations at schools, libraries, and community centers about the importance of pollinators.
- Garden Tours: Organizing tours of pollinator-friendly gardens.
Engaging with Local Schools
Engaging with local schools is another important way to educate the community about pollinators. This can involve:
- School Gardens: Helping schools to create pollinator-friendly gardens.
- Classroom Presentations: Giving classroom presentations about the importance of pollinators.
- Educational Materials: Providing schools with educational materials about pollinators.
Advocating for Pollinator-Friendly Policies
Advocating for pollinator-friendly policies is essential for creating long-term change. This can involve working with local governments to:
- Ban or Restrict Pesticides: Banning or restricting the use of pesticides that are harmful to pollinators.
- Protect Pollinator Habitat: Protecting existing pollinator habitat and creating new habitat.
- Promote IPM Practices: Promoting the use of integrated pest management (IPM) practices.
Working with Local Governments
Working with local governments can be an effective way to advocate for pollinator-friendly policies. This can involve:
- Attending City Council Meetings: Attending city council meetings to voice your concerns about pollinator conservation.
- Contacting Elected Officials: Contacting elected officials to urge them to support pollinator-friendly policies.
- Working with City Planners: Working with city planners to incorporate pollinator habitat into urban development projects.
The Role of Citizen Science
Citizen science projects can play a vital role in monitoring pollinator populations and gathering data on their distribution and abundance. These projects involve volunteers who collect data on pollinators in their local areas. The data collected by citizen scientists can be used to track changes in pollinator populations over time and to identify areas where pollinators are in decline.
Examples of Citizen Science Projects
There are many citizen science projects that focus on pollinators. Some examples include:
- The Great Sunflower Project: This project asks volunteers to count the number of pollinators that visit sunflowers in their gardens.
- Bumble Bee Watch: This project asks volunteers to identify and photograph bumble bees in their local areas.
- Monarch Watch: This project asks volunteers to tag monarch butterflies and track their migration.
Overcoming Challenges in Urban Environments
Attracting native pollinators to urban areas can be challenging due to factors such as limited space, poor soil quality, and high levels of pollution. However, there are many ways to overcome these challenges.
Addressing Soil Contamination
Soil contamination can be a major problem in urban areas. To address soil contamination, you can:
- Soil Testing: Test your soil to determine if it is contaminated.
- Soil Remediation: Remediate contaminated soil by removing it and replacing it with clean soil, or by using phytoremediation techniques.
- Raised Beds: Grow plants in raised beds filled with clean soil.
Dealing with Limited Space
Limited space can be a challenge in urban areas. To deal with limited space, you can:
- Vertical Gardening: Use vertical gardening techniques to grow plants on walls or fences.
- Container Gardening: Grow plants in containers on balconies or patios.
- Rooftop Gardens: Create a rooftop garden.
Mitigating Light Pollution
Light pollution can disrupt the behavior of nocturnal pollinators, such as moths. To mitigate light pollution, you can:
- Use Dark Sky-Friendly Lighting: Use light fixtures that direct light downwards and shield the bulb from view.
- Reduce Outdoor Lighting: Reduce the amount of outdoor lighting you use.
- Turn Off Lights When Not Needed: Turn off outdoor lights when they are not needed.
The Long-Term Benefits of Urban Pollinator Habitats
Creating pollinator habitats in urban areas has numerous long-term benefits. These benefits include:
- Increased Biodiversity: Pollinator habitats can increase biodiversity in urban areas by providing food and shelter for a variety of species.
- Improved Ecosystem Health: Pollinators play a vital role in maintaining the health of ecosystems. By supporting pollinator populations, we can improve the health of our urban ecosystems.
- Enhanced Food Security: Pollinators are essential for the production of many fruits, vegetables, and nuts. By supporting pollinator populations, we can enhance food security.
- Aesthetic Benefits: Pollinator gardens can add beauty and color to urban areas, making them more attractive and enjoyable places to live.
- Educational Opportunities: Pollinator gardens can provide educational opportunities for people of all ages, teaching them about the importance of pollinators and the role they play in our ecosystems.
Success Stories: Urban Areas Leading the Way
Many cities around the world are already taking steps to attract native pollinators to urban areas. Here are a few examples of successful initiatives:
- Chicago, USA: Chicago has implemented a number of initiatives to support pollinators, including planting pollinator-friendly gardens in parks and public spaces, and reducing pesticide use.
- Toronto, Canada: Toronto has created a network of pollinator gardens throughout the city, and has launched a public awareness campaign to educate residents about the importance of pollinators.
- London, UK: London has implemented a number of initiatives to support pollinators, including creating green roofs and walls, and planting pollinator-friendly plants along roadsides.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
Attracting native pollinators to urban areas is not just a nice thing to do; it is a necessity for the health of our ecosystems and the well-being of our communities. By creating pollinator-friendly habitats, reducing pesticide use, providing water sources, and educating the community, we can transform our cities into havens for pollinators and reap the numerous benefits they provide. Let’s work together to create a future where our cities are buzzing with life and our ecosystems are thriving.
Every small effort counts. Whether you plant a single flower box on your balcony, advocate for pesticide-free parks, or educate your neighbors about the importance of bees, you are making a difference. The future of our pollinators, and indeed, the future of our planet, depends on our collective action. Let’s get buzzing!